Safety and Feasibility of Anti-CD19 CAR T Cells Expressing Inducible IL-7 and CCL19 in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Large B-cell Lymphoma
Published in Immunology
Anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells have the potential to be a curative therapy for lymphoma patients. However, most patients either fail to respond to this treatment or relapse after achieving initial remission1-3. To improve the therapeutic benefits of CAR-T cells, many innovative CAR designs have been developed to enhance the antitumor efficiency and overcome treatment resistance related to inadequate expansion, infiltration, and persistence of CAR-T cells4-7. In this regard, fourth-generation CARs (referred to as “armored” CARs) that incorporate cytokines (IL-7, IL-15, or IL-21) are being developed to try to improve CAR-T cell persistence, tumor targeting, and antitumor capacity8-12. Another strategy is to modify CAR-T cells with the expression of a chemokine receptor or chemokine (CCL19, CCL21) that guides the CAR-T cells to the tumor site4,13. The feasibility of these strategies has been demonstrated in preclinical settings and evaluated in clinical trials across a range of malignancies14-16. Recently, anti-CD20 CAR-T cells expressing IL-7 and CCL19 have demonstrated enhanced antitumor activity compared to parental CAR-T cells and achieved complete elimination of pre-established solid tumors in mice15,16. Although preclinical evidences in different solid tumor models support the potential antitumor efficacy of armored CAR-T strategies, however, clinical results in humans are lacking.
In this study, Lei et al. developed a novel CAR-T therapy for patients with R/R LBCL by engineering CD19-specific CAR-T cells to secrete IL-7 and CCL19 (7 × 19 CAR-T cells) upon CD19 antigen engagement. IL-7 is a crucial T-cell homeostatic cytokine that plays essential roles in promoting T cells survival, expansion, and differentiation. CCL19 is a main chemokine that promotes leukocyte chemotaxis. Thus, 7 × 19 CAR-T cells were designed to co-express IL-7 to promote T-cell fitness and persistence and CCL19 to enhance the recruitment of leukocytes towards the tumor sites, thereby eliciting a potent and durable anti-lymphoma response against lymphoma(Figure 1) .
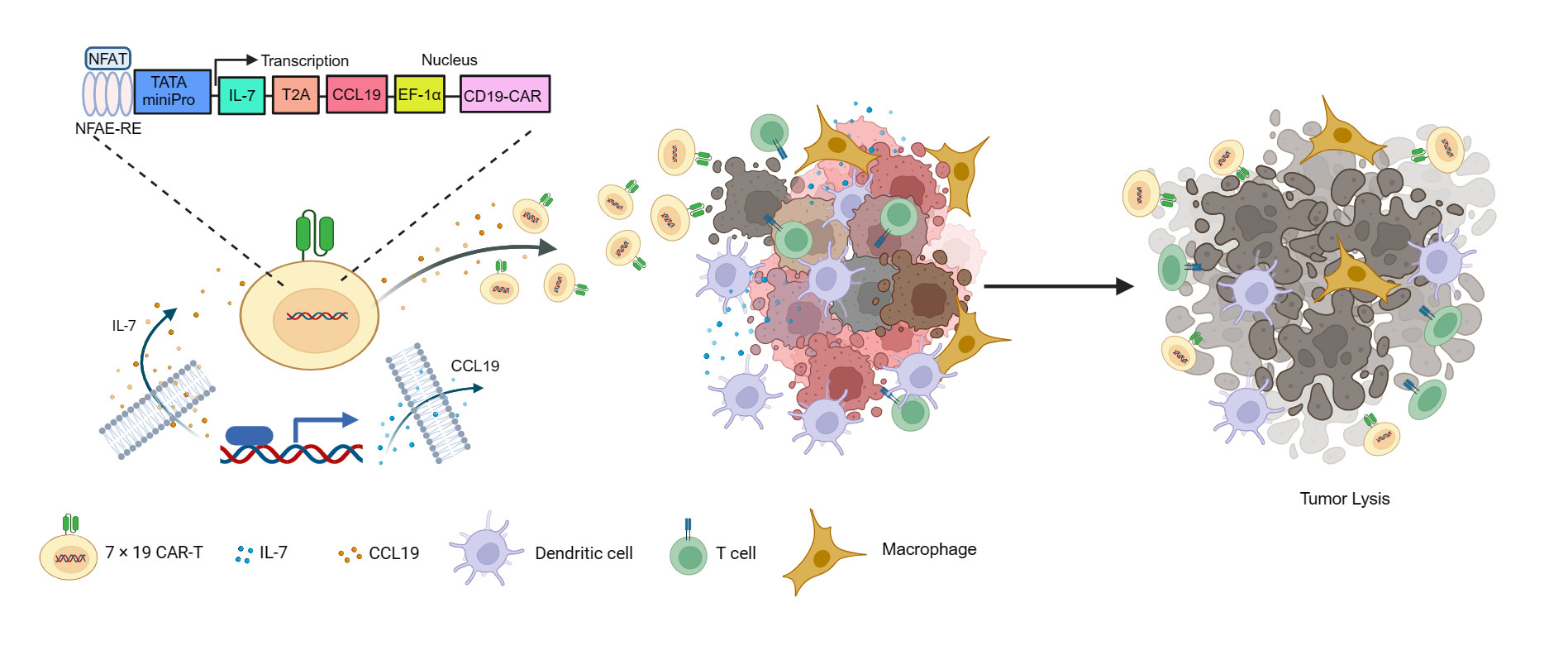 Figure 1. Schematic diagram of 7 × 19 CAR and its antitumoral model
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of 7 × 19 CAR and its antitumoral model
Indeed, the preclinical study demonstrated that 7 × 19 CAR-T cells exhibited dramatically increased proliferation, a high proportion of stem memory T cell (TSCM), enhanced migration capability, and improved in vitro and in vivo anti-lymphoma activity compared to conventional anti-CD19 CAR-T cells .
Furthermore, the phase 1 clinical trial of 7 × 19 CAR T cell therapy in patients with R/R LBCL showed only 12.8% and 10.3% ≥ grade 3 CRS and neurotoxicity, respectively, and achieved an overall response rate of 79.5% (complete remission, 56.4%; partial response, 23.1%) in patients with R/R LBCL, with PFS of 13 months and OS of 53.8% at 2 years .
Furthermore, they also found that some biomarkers are associated with clinical response and toxicity, such as IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-7, IL-13, IL-8, IFN-gamma-inducible protein-10 (IP-10), Macrophage inflammatory protein-1-beta (MIP-1β), Stromal cell-derived factor-1α (SDF-1α), and CCL19, and patients received high proportion of subtypes of TSCM CAR-T cells favoring better antitumor function .
These results indicate that 7 × 19 CAR-T cell therapy has not only a favorable safety profile but also superior efficacy against B-cell lymphoma to previously reported conventional anti-CD19 CAR T cell therapies. The study by Lei et al. suggests a significant clinical benefit of 7 × 19 CAR T-cell therapy for patients with R/R LBCL and supports 7 × 19 CAR T-cell therapy as a promising treatment strategy for B-cell malignancies.
REFERENCES
1 Locke, F. L. et al. Long-term safety and activity of axicabtagene ciloleucel in refractory large B-cell lymphoma (ZUMA-1): a single-arm, multicentre, phase 1-2 trial. Lancet Oncol 20, 31-42 (2019).
2 Schuster, S. J. et al. Tisagenlecleucel in Adult Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N Engl J Med 380, 45-56 (2019).
3 Neelapu, S. S. et al. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel CAR T-Cell Therapy in Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N Engl J Med 377, 2531-2544 (2017).
4 Rafiq, S., Hackett, C. S. & Brentjens, R. J. Engineering strategies to overcome the current roadblocks in CAR T cell therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 17, 147-167 (2020).
5 Wei, J. et al. Targeting REGNASE-1 programs long-lived effector T cells for cancer therapy. Nature 576, 471-476 (2019).
6 Chen, J. et al. Tuning charge density of chimeric antigen receptor optimizes tonic signaling and CAR-T cell fitness. Cell Res 33, 341-354 (2023).
7 Li, W. et al. Chimeric Antigen Receptor Designed to Prevent Ubiquitination and Downregulation Showed Durable Antitumor Efficacy. Immunity 53, 456-470 e456 (2020).
8 Pegram, H. J. et al. Tumor-targeted T cells modified to secrete IL-12 eradicate systemic tumors without need for prior conditioning. Blood 119, 4133-4141 (2012).
9 Hu, B. et al. Augmentation of Antitumor Immunity by Human and Mouse CAR T Cells Secreting IL-18. Cell Rep 20, 3025-3033 (2017).
10 Batra, S. A. et al. Glypican-3-Specific CAR T Cells Coexpressing IL15 and IL21 Have Superior Expansion and Antitumor Activity against Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Res 8, 309-320 (2020).
11 Zhou, J. et al. Chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR-T) cells expanded with IL-7/IL-15 mediate superior antitumor effects. Protein Cell 10, 764-769 (2019).
12 Xu, Y. et al. Closely related T-memory stem cells correlate with in vivo expansion of CAR.CD19-T cells and are preserved by IL-7 and IL-15. Blood 123, 3750-3759 (2014).
13 Li, H. et al. Targeting brain lesions of non-small cell lung cancer by enhancing CCL2-mediated CAR-T cell migration. Nat Commun 13, 2154 (2022).
14 Pang, N. et al. IL-7 and CCL19-secreting CAR-T cell therapy for tumors with positive glypican-3 or mesothelin. J Hematol Oncol 14, 118 (2021).
15 Adachi, K. et al. IL-7 and CCL19 expression in CAR-T cells improves immune cell infiltration and CAR-T cell survival in the tumor. Nat Biotechnol 36, 346-351 (2018).
16 Goto, S. et al. Enhanced anti-tumor efficacy of IL-7/CCL19-producing human CAR-T cells in orthotopic and patient-derived xenograft tumor models. Cancer Immunol Immunother 70, 2503-2515 (2021).
Follow the Topic
-
Cell Discovery

This journal aims to provide an open access platform for scientists to publish their outstanding original works and publishes results of high significance and broad interest in all areas of molecular and cell biology.
Ask the Editor - Immunology, Pathogenesis, Inflammation and Innate Immunity
Got a question for the editor about the complement system in health and disease? Ask it here!
Continue reading announcement





Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in