Shaping the Future of Medical Laboratory Practice in Somaliland: A Review of Current Standards
Published in Protocols & Methods, General & Internal Medicine, and Public Health
I've often wondered about the root causes of the deterioration of the healthcare sector, about the deep-rooted problems whose effects are embodied in the pain and suffering of patients, and extend beyond the fragile trust in its services. All those who are financially able cannot afford a healthcare facility except for treatment abroad...
Despite the marked discrepancy between the objective and subjective framework surrounding this deep-rooted problem, the majority of us are aware that everyone, without exception, is suffering...?!
What are the reasons, then...?
Despite the continuous and intensive efforts, and the utmost priority given to this sensitive service sector, and its essential and important focus, the results of the work that has continued for years remain very slight, almost negligible...!
When examining the underlying causes of this deterioration, and examining the complexities and difficulties associated with the healthcare system, the "scarcity of resources" is cited as the primary reason...!
________________________________
My curiosity to research the subject was piqued by what Professor Ayoub Al Hammadi wrote a while ago about the enormous loss a country like Yemen incurs as a result of the country's reluctance to access health services and travel abroad for treatment.
This matter caught my attention, and I began to question myself.
Are resources and a financial budget nonexistent?
It is important that they are not nonexistent.
Do quality, efficiency, and performance indicators require huge budgets to improve for the better?
If budgeting is a requirement, how can it be that countries with huge budgets allocated to improving and developing their health sectors and ensuring quality fail to achieve the desired results, while others succeed despite scarce resources and complex challenges?
For example, Rwanda, despite scarce resources and the genocide of 1994, was able to build a strong healthcare system, compared to what Kenya has achieved despite its abundant resources.
If so, what is the maximum budget required?
If we think deeply, we will find that the matter is like a vast, extended space that has no limits. You see the distant but cannot reach it. The closer someone tries, the further away it becomes.
________________________________
I still remember a discussion I had years ago with my older brother about the personal expenses we need on a daily basis. I was confused, and I asked him about something I didn't have an answer to at the time. I asked him, "Why does everyone, despite the varying amounts of their daily expenses, complain about their meagerness? I know people with significant financial capabilities and enormous expenses, and yet everyone still points to their meagerness...?!!" He said to me in simple words: "If a person were to create a path for himself, a million dollars wouldn't be enough for him for a day...!"
These words resonated deeply in my mind.
I sensed the importance of contentment followed by gratitude and thanks. Without them, a person would remain in a state of confusion and worry, even if he owned the whole world. In contrast, these words engraved the principle of governance as a necessity, and inspired me to believe that conscious management of what is available and accessible, as well as what is appropriate and required, is the key to solutions...
I understood that the issue is not related to quantity, but rather to quality...
These words served as a beacon illuminating my path during the research I conducted last year, and the questions I never ceased searching for answers to...
________________________________
When I began researching the causes of the deteriorating quality of healthcare, and my ongoing attempts to understand the context of the relentless challenges, I came across three fundamental axes deeply rooted in the context and hindering its optimal implementation, which are essential for its resolution:
1. Allocating resources based on evidence and data, and giving top priority to the fundamental pillar with the broadest impact and overall benefit...
Despite the complexity of the healthcare system and its components, and the interconnected and interdependent aspects, which make it difficult to prioritize its improvement, the widespread adoption of personalized medicine and patient-centered care (PMC) has proven the role of laboratory and diagnostics as a fundamental pillar for improving healthcare quality. However, the other challenge facing us here is the far-reaching planning and implementation, and achieving the desired goals and outcomes previously planned through effective and continuous movement through the context of challenges and the efficiency of performance in addressing them without interruption...
________________________________
Real-life experiences and the many roles I have played over the past year were sufficient to reach an important conclusion. The reality is that addressing the context comprehensively begins with the individual(s) connected to that context, without exception. This requires a dual approach to calibrating performance with greater efficiency and effectiveness.
This duality constitutes the two remaining key axes for moving the healthcare system toward optimal performance and quality:
2. Quality Management
3. Quality of Management, or more clearly, Quality of Leadership
Despite the importance of the three axes, in addition to the role played by modern digital technology, the quality of management and quality leadership is the fundamental aspect upon which the first two axes are based and built. Successfully improving and developing the healthcare system requires leadership with a sustainable, long-term vision, goals that serve future generations, and the continuation of efforts despite failure, without ceasing despite the success achieved, achieving qualitative change in the healthcare system and ensuring its reliability.
________________________________
Today, I share a detailed summary and results of the past year's intensive efforts, as well as another research achievement on the context of medical laboratory practices in African countries in general and Somaliland in particular. The research is titled:
Shaping the Future of Medical Laboratory Practice in Somaliland: A Review of Current Standards.
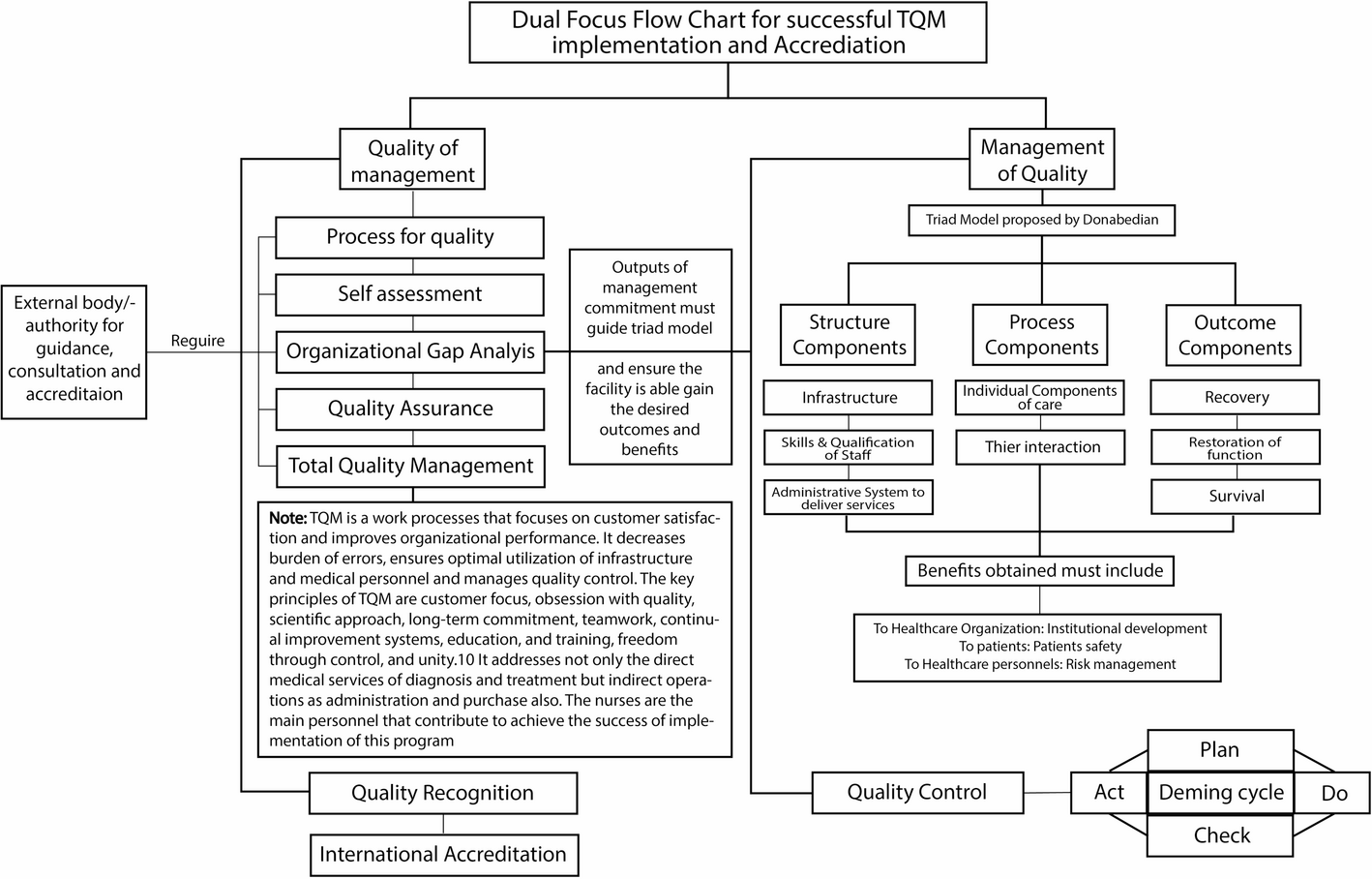
The research highlights the importance of compliance with standards, the impact of such compliance on improving the healthcare system, and the essential role of the laboratory department in building accreditation and quality assurance as a whole. It also discusses the various standards frameworks adopted, and the gap represented by the lack of an agreed-upon, comprehensive framework. The research also highlights the importance of a comprehensive standards framework, which ensures compliance with the following standards:
Management of Quality Standards
Quality of Management Standards.
For more details, the research link is available in the comments...
Thanks to #GHF Team and everyone who worked, contributed, and collaborated in the success of this publication. Grateful for the extensive efforts you put in to ensure this success.
Follow the Topic
Standards
Life Sciences > Biological Sciences > Biological Techniques > Computational and Systems Biology > Standards
Health Policy
Life Sciences > Health Sciences > Public Health > Health Policy
Policy Implementation
Humanities and Social Sciences > Politics and International Studies > Public Policy > Policy Implementation
Policy Formulation
Humanities and Social Sciences > Politics and International Studies > Public Policy > Policy Formulation
Regulation and Industrial Policy
Humanities and Social Sciences > Economics > Public Economics > Regulation and Industrial Policy
Laboratory Medical Diagnosis
Life Sciences > Health Sciences > Clinical Medicine > Diagnosis > Laboratory Medical Diagnosis
-
Discover Applied Sciences

This is a multi-disciplinary, peer-reviewed journal for the disciplines of Applied Life Sciences, Chemistry, Earth and Environmental Sciences, Engineering, Materials Science and Physics, fostering sound scientific discovery to solve practical problems.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Engineering: Energy Management System
Power system energy management is performed at different levels with different aims. The most important goals of optimal energy management of the power systems are cost reduction, reduce emissions, improve reliability and power quality indexes, increase profitability, etc. Innovative methods can be used to provide an energy management plan, or energy management can be defined as an optimization problem and optimization algorithms can be used to solve it. Uncertainties are also very important issues in power system operation programs, especially in the lower levels of the power system (microgrids). The electric vehicle parking lots or aggregators can also be used in the microgrids to store energy, in which case the issue of energy management takes on a new face. Therefore, to provide a good energy management program for the power system, one must have a detailed knowledge of its components and the technical constraints of the power system. Therefore, to provide a good energy management program, a comprehensive model of the power system with detailed data should be provided.
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Jun 30, 2026
Engineering: Computer Aided Engineering Design, Manufacturing and Maintenance
The collection bridges the gap between traditional engineering practices and the latest technological advancements. Spanning from the intricate scale of materials to the broader dimensions of structures and systems, this collection offers a panoramic view of the engineering landscape. Open to a diverse range of engineering disciplines, it welcomes contributions from areas such as Mechanical Engineering, Aerospace Engineering, Chemical Engineering, Environmental Engineering, Nuclear Engineering, Automotive Engineering, and Civil Engineering. Central to the collection is the integration of time-tested traditional methodologies with modern innovations like additive manufacturing and digital twins. Topics of interest include design simulations (single- or multi-scale), precision manufacturing, system maintenance, and the harmonization of legacy systems with contemporary tools, all while emphasizing the importance of understanding materials and their influence on larger structures and systems. By offering a blend of foundational knowledge and cutting-edge insights, this collection serves as an invaluable resource for authors aiming to showcase their research and readers keen on understanding the evolution of engineering practices.
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Jun 30, 2026






Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in