System with Thermal Management for Synergistic Water Production, Electricity Generation and Crop Irrigation
Published in Materials and Mechanical Engineering

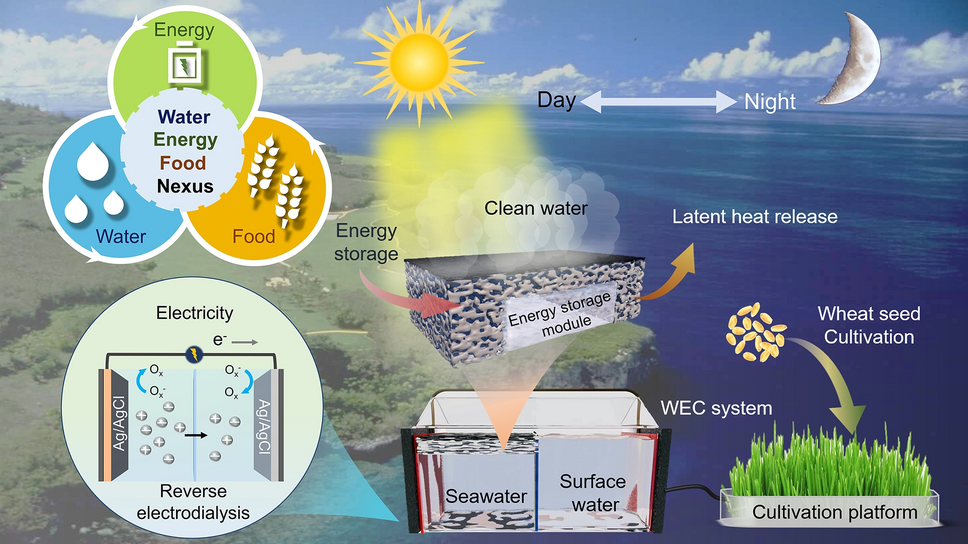
As global water, energy and food demands intensify under climate change, a scalable, round-the-clock technology that simultaneously produces fresh water, electricity and irrigation water is urgently needed. Now researchers from Harbin Institute of Technology, Wuhan University and Tsinghua University—led by Prof. Shih-Hsin Ho—have unveiled an integrated Water/Electricity-Cogeneration–Cultivation (WEC) platform that couples solar-driven desalination with salinity-gradient power generation and zero-pollution crop irrigation. The work offers a practical blueprint for advancing the water–energy–food (WEF) nexus toward carbon-neutral sustainability.
Why WEC Matters
- 24 h Operation: An energy-storage hydrogel evaporator (ESE) sustains 1.91 kg m-2 h-1 evaporation under 1 sun and 0.54 kg m-2 h-1 in darkness, eliminating daylight-only bottlenecks.
- Triple Electricity Gain: Reverse electrodialysis (RED) harvests ~0.30 W m-2 from desalination-enhanced brine—three-fold higher than conventional seawater/river-water RED.
- Zero-Discharge Irrigation: System drainage irrigates wheat seedlings (shoot ≈ 87 mm, root ≈ 80 mm within 7 d) without secondary contaminants, closing the WEF loop.
- Carbon Offset: One-year operation offsets 1,362.52 kg CO2e, equivalent to burning 1,172 m3 of natural gas.
Innovative Design & Features
- Thermal-Management Evaporator: PVA hydrogel embedded with n-octadecane microcapsules stores daytime waste heat and releases it after sunset, extending effective evaporation by ~1 h.
- Bio-Graphene Photothermal Layer: Super-hydrophobic surface (153° WCA) on melamine sponge enables rapid solar-thermal localization (>49 °C) while inner hydrophilic networks pump water continuously.
- Salinity-Gradient Engine: Desalination continuously boosts brine concentration (3.5 → 5.8 wt%), driving RED open-circuit voltage from 175 to 221 mV and stabilizing power at 0.3 W m-2.
- Mechanical Durability: 30 thermal cycles and 21-day continuous operation show no performance decay; compressive strength ~0.19 MPa with full shape recovery.
Applications & Future Outlook
- All-Weather Water–Power Coupling: Field tests under natural light/dark cycles deliver 9.37 kg m-2 fresh water and 0.29 W m-2 electricity per day—30 % more water than non-storage controls.
- Irrigation without Salt Stress: Drainage Na+ (552.8 mg L-1) is <1/60 of seawater; wheat germination and biomass match surface-water controls, validating safe reuse.
- Carbon-Neutral Potential: Daytime electricity generation contributes 54 % of total GHG offsets; thermal management alone adds 349 kg CO2e yr-1(26 % bonus).
- Scalability Roadmap: Efficiency can be further lifted via hierarchical water channels, >95 % light-absorbing metamaterials, aerogel insulation and thinner ion-exchange membranes.
This comprehensive study demonstrates that synergistic thermal engineering, desalination and salinity-energy recovery can simultaneously tackle water scarcity, clean-electricity deficits and food irrigation. It provides a readily deployable, low-cost route toward resilient WEF security and global carbon-neutrality goals. Watch for more advances from Prof. Shih-Hsin Ho’s team at Harbin Institute of Technology!
Follow the Topic
-
Nano-Micro Letters

Nano-Micro Letters is a peer-reviewed, international, interdisciplinary and open-access journal that focus on science, experiments, engineering, technologies and applications of nano- or microscale structure and system in physics, chemistry, biology, material science, and pharmacy.





Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in