The natural product tubeimoside I impedes cervical cancer metastasis by stabilizing HDAC5 and suppressing the H3K27ac/KPNA2 axis
Published in Cancer and Pharmacy & Pharmacology
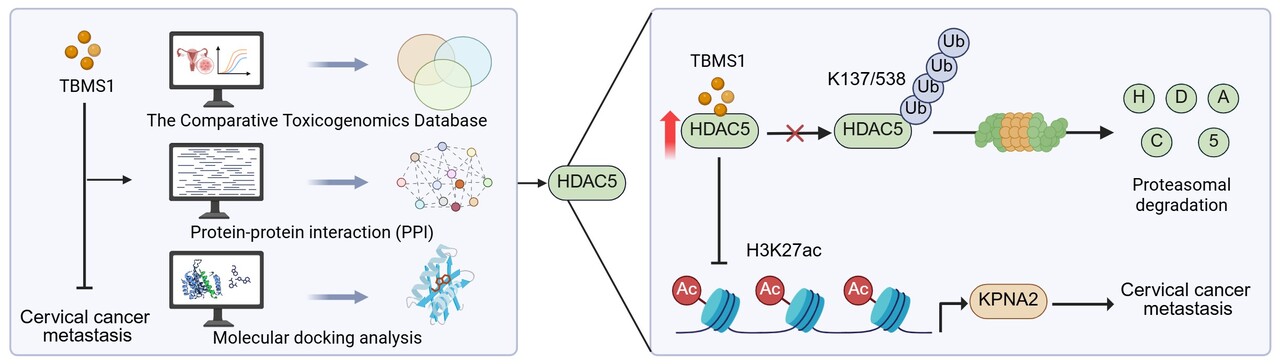
The development of traditional Chinese medicine spans thousands of years, while its modern systematic research applied to cancer therapies commenced in the latter half of the 20th century. Numerous studies have emerged elucidating the effects and mechanism of actions of traditional Chinese medicine in treating tumors [1]. The traditional Chinese medicine-derived agents exert antitumor effects through various pathways, such as inducing cell death of tumor cells, modulating the tumor microenvironment, or acting synergistically to enhance sensitivity of other treatments [2-4]. As a traditional Chinese herbal medicine, TBMS1 also exhibits anticancer effect. We previously demonstrated TBMS1 promotes autophagy-related cell death in cervical cancer [5]. Nevertheless, whether and how TBMS1 inhibits the metastasis of cervical cancer remains unknown. To our surprise, we observed a clear dose dichotomy: high dose of TBMS1 induces autophagy and cell death, while low dose of TBMS1 inhibits the migration and invasion of cervical cancer cells without affecting cell proliferation.
Based on this premise, we employed computer-aided virtual screening to identify potential binding targets of TBMS1, among which histone deacetylase 5 (HDAC5) emerged as a top-ranked candidate molecule. The role of HDAC5 in cancer is context-dependent, and its specific function in cervical cancer remains unclear. Through cellular thermal shift assay (CETSA) drug affinity responsive target stability (DARTS) assay, and ubiquitination experiments, it was found that TBMS1 binds to HDAC5 and protects its lysine 137 and lysine 538 from ubiquitination, thereby blocking the proteasomal degradation pathway of HDAC5. This stabilization leads to an increase in HDAC5 protein level, consequently resulting in decreased acetylation of histone H3 at lysine 27 (H3K27ac), a modification marker associated with gene expression activation [6]. RNA sequencing analysis further identified karyopherin subunit alpha 2 (KPNA2), a known metastasis-promoting protein, as a key downstream target of H3K27ac. TBMS1-mediated HDAC5 upregulation reduces the enrichment of H3K27ac at KPNA2’s promoter region. Functional experiments confirmed that overexpressing KPNA2 reverses the inhibitory effect of TBMS1 on the migration and invasion of cervical cancer cells.
Our study clarifies the role of HDAC5 as a metastasis suppressor in cervical cancer, which contrasts with its reported oncogenic functions in several other tumor contexts. The contrary effects of HDAC5 on cancer might be attributed to the different deacetylated client proteins or cancer types. More importantly, it reveals that TBMS1’s anti-metastatic activity is separable from its cytotoxic effects, depending entirely on dose. This duality suggests a potential therapeutic strategy: low dose of TBMS1 could be used to specifically target metastasis, possibly in adjuvant or maintenance settings, while high dose of TBMS1 could be reserved for tumor debulking. This study not only deepens the understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying the antitumor effects of TBMS1, but also provides a refined, dose‑based direction for its future development as a tumor therapeutic agent.
- Wong, R., C.M. Sagar, and S.M. Sagar, Integration of Chinese medicine into supportive cancer care: a modern role for an ancient tradition. Cancer Treat Rev, 2001. 27(4): p. 235-46.
- Jia, W., J. Yuan, B. Cheng, and C. Ling, Targeting tumor-derived exosome-mediated premetastatic niche formation: The metastasis-preventive value of traditional Chinese medicine. Cancer Lett, 2023. 567: p. 216261.
- Xun, Y., G. Chen, G. Tang, C. Zhang, S. Zhou, T.L. Fong, et al., Traditional Chinese medicine and natural products in management of hepatocellular carcinoma: Biological mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Pharmacol Res, 2025. 215: p. 107733.
- Zhao, W., X.D. Zheng, P.Y. Tang, H.M. Li, X. Liu, J.J. Zhong, et al., Advances of antitumor drug discovery in traditional Chinese medicine and natural active products by using multi-active components combination. Med Res Rev, 2023. 43(5): p. 1778-1808.
- Feng, X., J. Zhou, J. Li, X. Hou, L. Li, Y. Chen, et al., Tubeimoside I induces accumulation of impaired autophagolysosome against cervical cancer cells by both initiating autophagy and inhibiting lysosomal function. Cell Death Dis, 2018. 9(11): p. 1117.
- Vaquero-Sedas, M.I. and M. Vega-Palas, Targeting Cancer through the Epigenetic Features of Telomeric Regions. Trends Cell Biol, 2019. 29(4): p. 281-290.
Follow the Topic
-
British Journal of Cancer

This journal is devoted to publishing cutting edge discovery, translational and clinical cancer research across the broad spectrum of oncology.





Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in