TPE-Embedded Butterfly Bis-Crown Ether with Controllable Conformation and Supramolecular Chiroptical Property
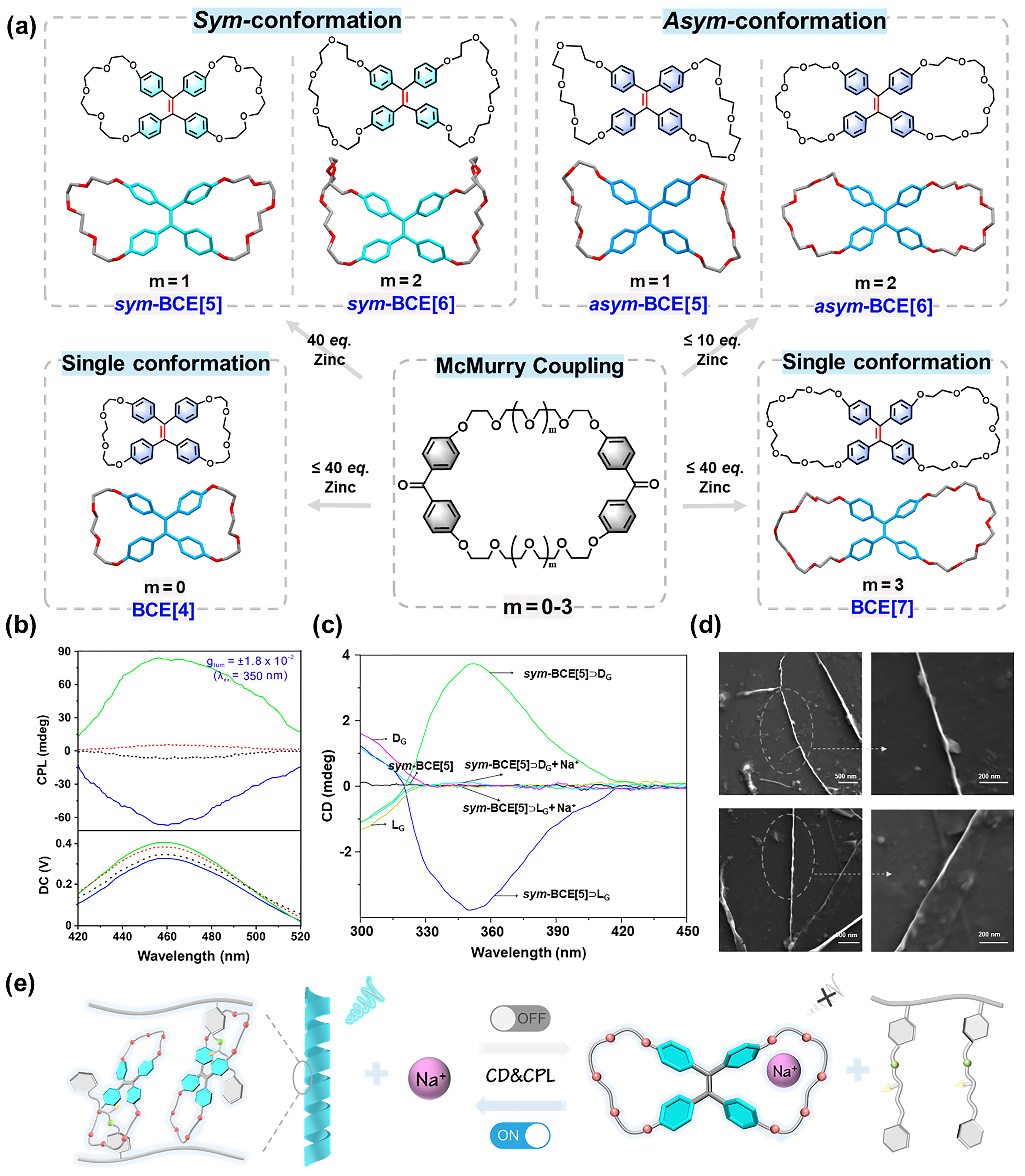
Our work presents a series of tetraphenylethylene (TPE)-embedded butterfly bis-crown ether macrocycles (BCE[n], n = 4-7). The presence of flexible oligoethylene chains with varying lengths was found to influence molecular conformation via multiple intramolecular interactions, resulting in the formation of two stabilized conformers with specific semi-rigid symmetric/asymmetric structures. Interestingly, these conformers display distinct fluorescence properties and host-guest binding abilities, and only sym-BCE[5] can serve as a host for chiral polymer binding. Moreover, both circular dichroism (CD) and circularly polarized luminescence (CPL) signals of the obtained assemblies could be switched off by the addition of sodium ion (Na+), suggesting potential applications in dynamic chiral materials.
Motivation
Tetraphenylethylene (TPE) is widely recognized as one of the most prevalent moieties with aggregation-induced emission (AIE) activity, making it an ideal fluorescent building block for integration into macrocycles. It is worth noting that a TPE derivative inherently possesses a diverse range of conformations, which are determined by the varying dihedral angles within its core structure. And the modulation in these conformational changes can consequently lead to variable photophysical properties. By precisely manipulating the dihedral angles in AIE compounds, these molecules with diverse conformations hold great potential for precise control over material functionalities. However, achieving distinct conformations for TPE compounds has proven to be an arduous challenge thus far, and the underlying chemistry governing these conformations remains enigmatic. This intriguing puzzle has ignited our motivation to embark on this research endeavor.
Our discovery
We synthesis of a series of TPE-based bis-crown ethers (BCE[n], n = 4-7) via intramolecular McMurry coupling interaction. To achieve AIE-active macrocycles with distinct conformations in both solution and solid state, we introduced chains with appropriate length to connect the phenyl-substituents, thereby constraining the dihedral angles. The cyclization of the TPE unit through flexible ethylene glycol chains revealed that varying chain lengths resulted in different degrees of distortion in the TPE core due to intramolecular tension. The incorporation of flexible side chains into the rigid TPE core induced specific strain on the molecules, resulting in two conformers existing in the semi-rigid BCE[5] and BCE[6], depending on the chain length. Additionally, they can be effectively purified using conventional column chromatography techniques. Due to subtle differences in conformation and ring size, their unique host-guest selective binding behaviors as well as their photophysical properties were systematically investigated. Furthermore, it was observed that only sym-BCE[5] exhibited the ability to act as a host for chiral polymeric guest binding, thereby facilitating the generation of chiral materials with controllable handedness through supramolecular chiral amplification induced by host-guest interaction.
Implications
Our findings highlight the significance of exploring conformational diversification in unraveling the exceptional characteristics of supramolecular macrocycles, while offering valuable insights into their structure-property relationships.
Follow the Topic
-
Nature Communications

An open access, multidisciplinary journal dedicated to publishing high-quality research in all areas of the biological, health, physical, chemical and Earth sciences.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Women's Health
Publishing Model: Hybrid
Deadline: Ongoing
Advances in neurodegenerative diseases
Publishing Model: Hybrid
Deadline: Mar 24, 2026






Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in