Ultra-simplified diffraction-based computational spectrometer
Published in Physics
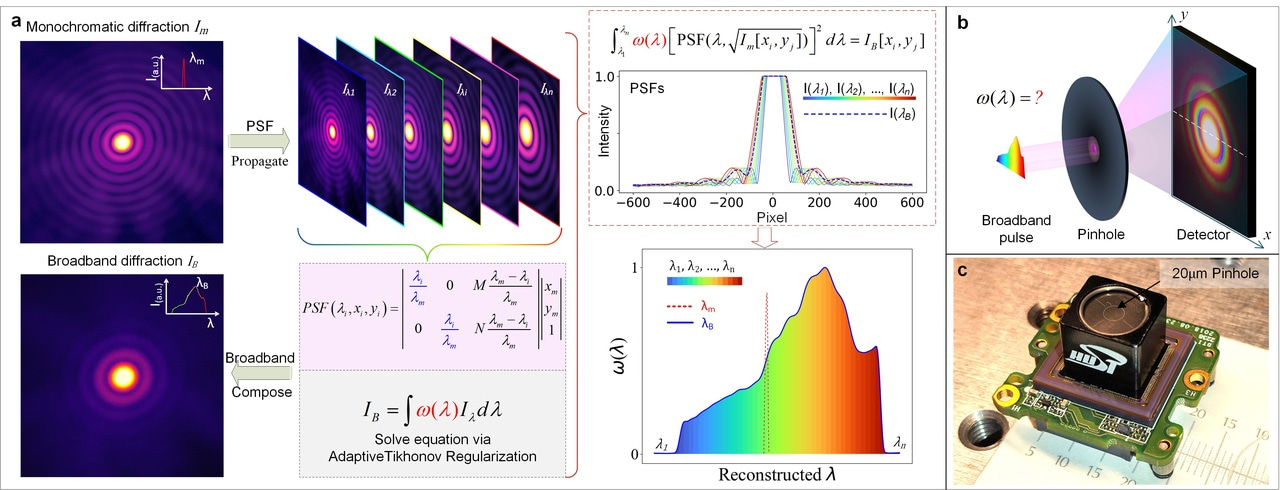
Miniaturizing spectrometers for mobile platforms has been a significant challenge in spectroscopy research. Previous designs often relied on intricate dispersion, high-precision fabrication, and complex calibration. Recently, we have demonstrated a compact spectrometer design with ultra-simplified architecture, offering a comprehensive alternative to current state-of-the-art compact computational spectrometers [1].
Inspired by the mono coherent diffractive imaging (CDI) approach introduced by Huijts et. al in 2020 [2], we propose a novel one-to-broadband diffraction decomposition strategy in computational spectrometer, facilitated by a numerical regularized transform using a spectral-point-spread-function (PSF) derived exclusively from the spectrumof the diffracted radiation. Our design introduces a conceptual leap in coherent mode decomposition with a PSF, rendering the architecture ultra-simplified and cost-effective. By employing a numerical regularized transform based on a single-shot measurement of quasi-monochromatic diffraction as the PSF, we eliminate the need for complex spectral encoding and calibrations. This streamlined design offers versatility for miniaturized, cost-effective, and lab-on-chip integrations.
A primary achievement of our method lies in its unprecedented compatibility, delivering wide bandwidth and precise spectral measurements. Our spectrometer achieves a reconstructed spectral peak precision of less than 1 nm over a 200 nm bandwidth, coupled with remarkable resolution for peaks within 3 nm separation. This level of performance is achieved from a single shot of a broadband diffraction pattern, bypassing the need for intricate dispersion designs and meticulous fabrications.
Notably, our innovative approach incorporates an arbitrarily shaped pinhole as a diffraction-based partial-disperser, positioned in front of the detector. This eliminates the need for intricate pre-encoding designs, making the spectrometer ultra-simplified and highly cost-effective, with a core disperser device priced at nearly one dollar.
Authors: Chuangchuang Chen, Honggang Gu, Shiyuan Liu.
References
[1] C. Chen, H. Gu, and S. Liu, "Ultra-simplified diffraction-based computational spectrometer," Light Sci. Appl. 13, 9 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-023-01355-4
[2] J. Huijts, S. Fernandez, D. Gauthier, M. Kholodtsova, A. Maghraoui, K. Medjoubi, A. Somogyi, W. Boutu, and H. Merdji, "Broadband coherent diffractive imaging," Nat. Photonics 14, 618–622 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-020-0660-7
Follow the Topic
-
Light: Science & Applications

A peer-reviewed open access journal publishing highest-quality articles across the full spectrum of optics research. LSA promotes frontier research in all areas of optics and photonics, including basic, applied, scientific and engineering results.
Your space to connect: The Polarised light Hub
A new Communities’ space to connect, collaborate, and explore research on Light-Matter Interaction, Optics and Photonics, Quantum Imaging and Sensing, Microscopy, and Spectroscopy!
Continue reading announcement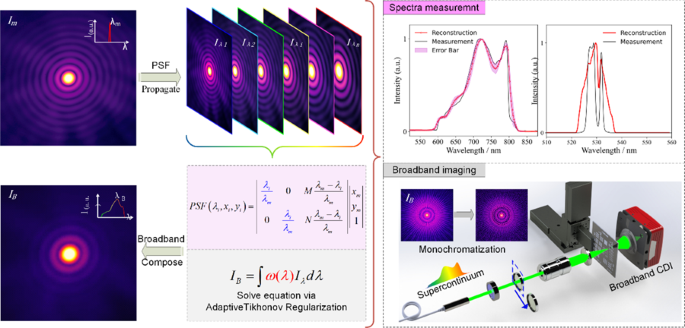
Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in