Unveiling Trust in Digital Healthcare
Published in Healthcare & Nursing, Social Sciences, and Behavioural Sciences & Psychology

Digital health holds the promise to transform healthcare by enhancing person-centred care and facilitating collaboration among multidisciplinary teams. However, despite these advantages, the sustainable implementation of digital healthcare remains challenging. One crucial factor influencing the adoption and effective use of digital health technologies is trust. Yet, the dimensions of trust in digital healthcare are not well-understood, limiting the development of standardized and robust measurement tools.
To address this gap, we conducted a comprehensive evidence review to identify instruments that measure trust and the key factors influencing consumers' trust in digital healthcare. Our findings shed light on how trust is defined, measured, and how these factors may impact outcomes, providing a foundation for improving trust in digital healthcare systems.
Mapping Trust in Digital Healthcare
We analysed 49 studies published between 2010 and 2023 that measured trust in digital healthcare. Of these, 46 focused on consumers' perspectives, with most research conducted in China and the United States. This geographical concentration highlights the need to consider cultural differences when applying trust measurement instruments across diverse populations. For instance, in China, where digital privacy is more regulated, perceptions of trust may differ significantly from those in Western countries.
Trust is an abstract, complex and relational construct, making it inherently difficult to define and measure. We found a wide variety of definitions across the studies, including trust-related processes (e.g., concerns about data accuracy), willingness to rely on digital healthcare, and the role of trust in facilitating interpersonal relationships. Surprisingly, over 40% of the studies did not provide a clear definition of trust, underscoring the need for conceptual clarity.
How Is Trust Measured?
Our study revealed that trust in digital healthcare is often measured using pre-existing instruments (75%), adaptations from non-health-related sources, or newly developed items not linked to any trust reference. This fragmented approach falls short of psychometric best practices, which emphasize rigorous development and validation processes tailored to specific populations and contexts.
Further, measuring trust should account for the unique characteristics of different digital health modalities they are designed for. For example, trust in remote patient monitoring ought to cover perceptions of data accuracy from wearable devices while trust in eConsults should cover the transferability of trust from the referring provider to the specialist. Without these context-specific instruments, capturing the nuances of trust in different digital health settings will continue to be challenging.
What Shapes Consumers' Trust?
Our findings indicate that both personal and interpersonal factors influence consumers' trust in digital healthcare. Key personal factors include digital literacy, education levels, prior experiences with digital health, satisfaction, and income. On the interpersonal level, the quality of the digital healthcare intervention, data accuracy, and customization play pivotal roles in shaping trust.
Conversely, perceived risks and privacy concerns negatively affect trust, while human interaction within automated interventions positively influences it. Notably, consumers' trust in healthcare providers can extend to the digital services they endorse, making healthcare provider trust a critical target for trust-building efforts.
Why Trust Matters?
Trust in digital healthcare is not merely a theoretical concern – it has tangible impacts on consumer behaviour. Our review found that trust positively correlates with consumers' intention to use, adopt, and find digital health technologies useful. In essence, fostering trust can facilitate the broader adoption of digital health innovations.
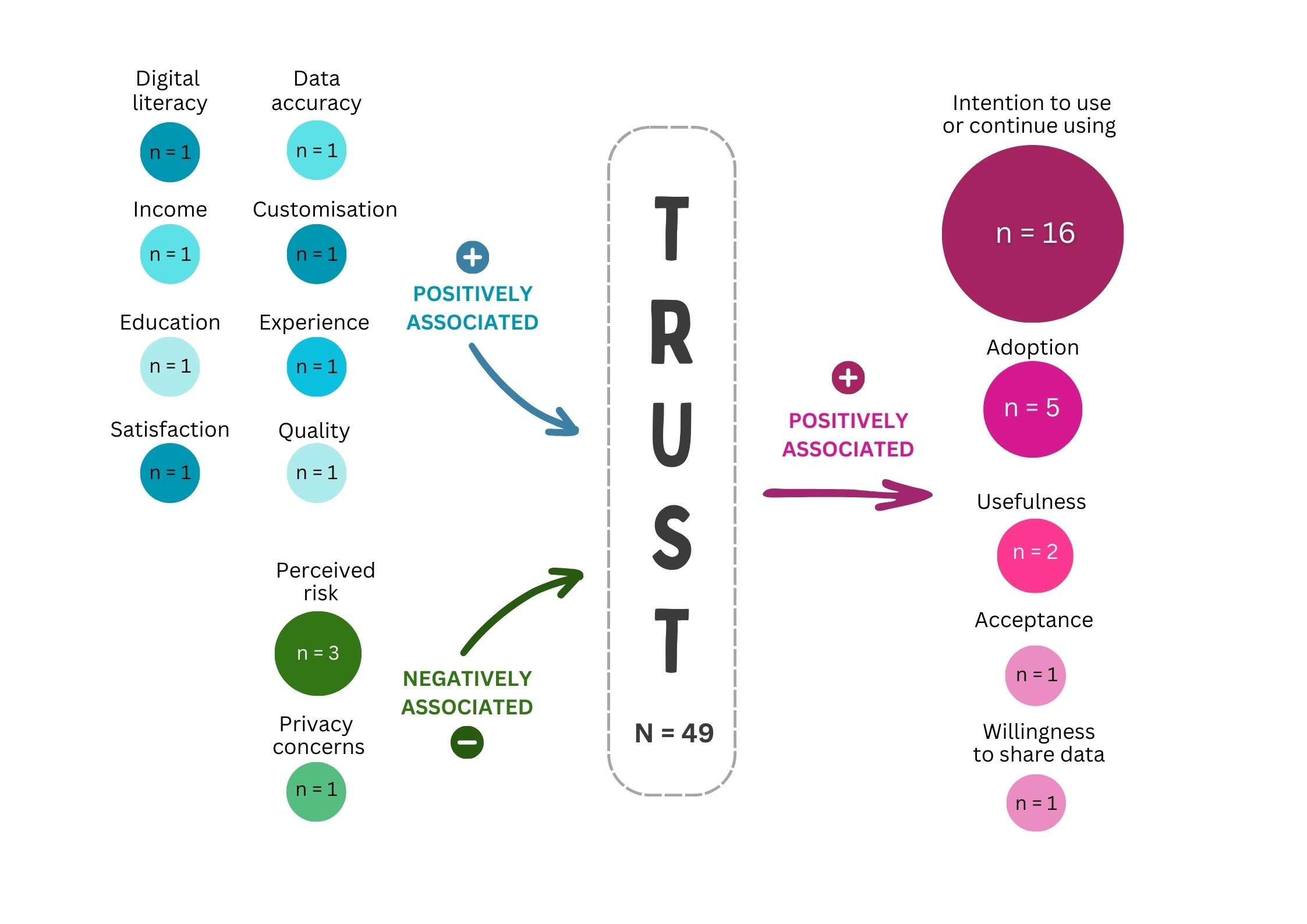
Factors and outcomes associated with consumers' trust in digital healthcare, with the number of studies that reported this result.
Bridging the Trust Gap
This is an important step toward understanding and measuring trust in digital healthcare. Developing a comprehensive framework for trust requires clear definitions, context-specific measurement tools, and consideration of the diverse factors influencing trust.
By fostering trust in digital healthcare systems, we can bridge the gap between innovation and sustainable implementation. This, in turn, enhances the adoption of digital health technologies, supports better health outcomes, and strengthens the long-term sustainability of digital healthcare solutions.

Follow the Topic
-
npj Digital Medicine

An online open-access journal dedicated to publishing research in all aspects of digital medicine, including the clinical application and implementation of digital and mobile technologies, virtual healthcare, and novel applications of artificial intelligence and informatics.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Digital Health Equity and Access
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Mar 03, 2026
Evaluating the Real-World Clinical Performance of AI
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Jun 03, 2026




Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in