Vesiclemia
Published in Cancer

Explore the Research
Vesiclemia: counting on extracellular vesicles for glioblastoma patients - Oncogene
Oncogene - Vesiclemia: counting on extracellular vesicles for glioblastoma patients
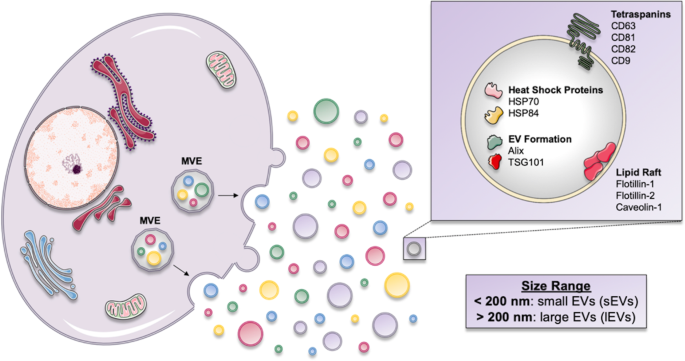
Vesiclemia is expressed in particles/mL and can be measured by at least two different and complementary methods, according to the International Society of Extracellular Vesicles (ISEV) recommendations:
- Electron microscopy or atomic force microscopy, with close-up and wide field provided
- Single particle analysis techniques, such as tunable resistive pulse sensing (TRPS), single particle tracking analysis and interferometry.
- Biochemical techniques, such as ELISA.
We also reiterate few hints on storage, minimal volume and pre-processing of the samples.
The use of this scientific term will foster bench-to-bedside communication and might help in providing a rigorous magnitude of concentrations to set the scale for hyper and hypovesiclemia. Knowing the level of circulating vesicles might then be considered as a diagnostic biomarker to inform on health conditions and pathological changes in homeostasis.
Follow the Topic
-
Oncogene

This journal aims to make substantial advances in our knowledge of processes that contribute to cancer by publishing outstanding research.





Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in