What Lies Beneath: How Microbes Evolve, Form New Ecotypes, and Increase Productivity
Published in Ecology & Evolution and Microbiology

Methane is produced naturally – expelled by wetlands, wild animals, and other sources – and via manmade sources like agriculture and fossil fuel production and use. While not as abundant as carbon dioxide in our atmosphere, methane traps significantly more heat, making it a critical-to-understand component in climate change.
In the Institute for Systems Biology’s Baliga Lab, we examined representative organisms of two classes of microbes whose interaction contributes to the conversion of more than 1 gigaton of carbon into methane every year. Our work was published in Nature Communications.
We discovered that gene mutations selected over a relatively short timeframe in the two microbes – Desulfovibrio vulgaris (Dv) and Methanococcus maripaludis (Mm) – led to distinct functions, specifically ecotypes or sub-populations that were more specialized to either an attached or a floating lifestyle.
This work shows that ecotypes of the same species can emerge over very short evolutionary timescales to specialize and collaborate with ecotypes of other species to significantly increase the productivity of ecologically important functions, such as methane production.
Lab Work
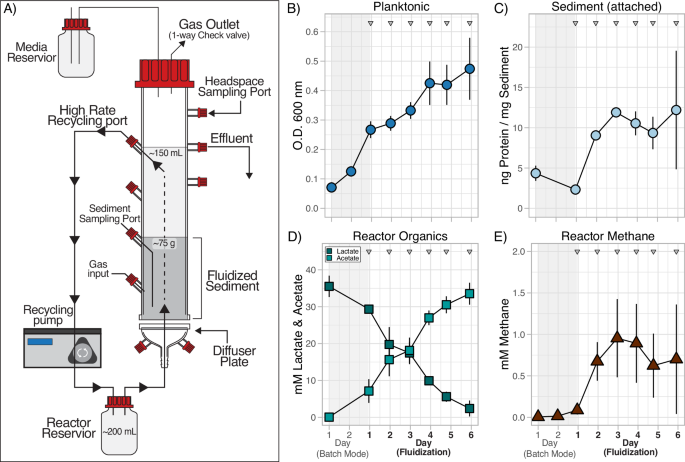
We started by building a customized fluidized bed reactor to simulate the soil subsurface, wherein methane-producing microbial communities are typically found. The reactor uses an up-flow current to “fluidize” a bed of solid particles into a suspension, akin to how soil particles are suspended in flowing groundwater in the subsurface. This reactor system allowed ISB scientists to examine complex microbial interactions that normally occur in the soil subsurface but in a controlled laboratory experiment.
Using this reactor system, we discovered that just a handful of mutations that were selected within 300-1,000 generations (for reference, months in the lab) of growing Dv and Mm as a microbial community in an obligate relationship had generated new ecotypes of each organism, where each ecotype had specialized to carry out specific roles in the simulated subsurface environment.
New ecotypes of Dv that had specialized to survive as biofilm attached to a sediment particle utilized more lactate, generating a byproduct of molecular hydrogen (H2) that nearby ecotypes of attached Mm could only partially utilize. The unused H2 was then scavenged by free-flowing Mm ecotypes, and used for producing a large amount of methane.

This novel study shows how few mutations are needed to generate ecotypes of microorganisms specialized to new environmental niches. Our findings further show that the synergistic interplay among ecotypes of diverse microbes across space and time can dramatically improve the productivity of the entire microbial community. In so doing, this study provides insight into the remarkable ability of microbial communities to adapt, specialize, and collaborate to profoundly influence the biogeochemical cycling of gigatons of major elements like carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus that are essential for sustaining life on Earth.
Next steps
Our findings underscore the importance of the enormous genetic diversity of microbes within a microbiome, be it from soil, oceans, or the human gut.
While current DNA sequencing technologies have the sensitivity and resolution to uncover the genetic diversity within a microbiome, we do not yet have the microbiological and computational tools needed to fully interpret the functional meaning of this diversity.
Our study illustrates the importance of investigating genomic diversity within microbiomes from a spatial, temporal, and functional context, as interactions among ecotypes of different species across these three axes may have important implications on how we diagnose health from disease or select the right mix of ecotypes of different species to use as pre/probiotics to restore the health of an ecosystem.
By Jacob Valenzuela, PhD, Senior Research Scientist, ISB and Nitin Baliga, MSc, PhD, SVP, Director and Professor, ISB.
Follow the Topic
-
Nature Communications

An open access, multidisciplinary journal dedicated to publishing high-quality research in all areas of the biological, health, physical, chemical and Earth sciences.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Women's Health
Publishing Model: Hybrid
Deadline: Ongoing
Advances in neurodegenerative diseases
Publishing Model: Hybrid
Deadline: Mar 24, 2026

Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in