Stopping life-threatening bleeding: A next-generation hemostatic solution in trauma care
Published in Bioengineering & Biotechnology, Materials, and Biomedical Research
The following video contains footage of live surgery, including severe bleeding, open wounds, and blood loss. Viewer discretion is advised.
-
Uncontrolled bleeding is a leading cause of preventable deaths worldwide, especially in traumatic injuries where time is critical. Imagine a scenario where a soldier on the battlefield or a car accident victim is bleeding profusely from a deep wound. Traditional methods to stop bleeding, like applying pressure or using gauze, often fall short in severe cases. This is where our research comes in.
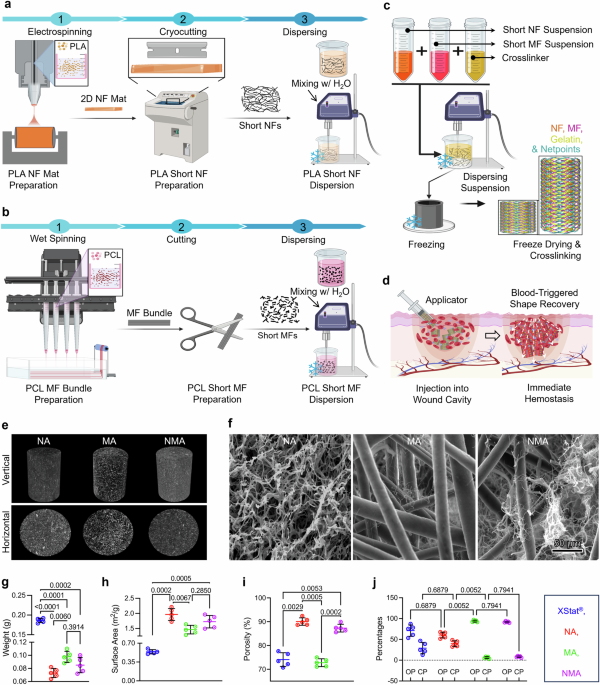
In a recent study published in Nature Communications, we developed a groundbreaking injectable material that can rapidly stop life-threatening bleeding. Using a unique nano- and microfiber aerogel (NMA) made from biodegradable polymers, we created a lightweight, sponge-like material that can be injected directly into a wound. Once inside, it expands to fill the cavity, absorbs blood, and triggers the body’s natural clotting process—all within seconds.
To show how this works, we conducted a study in a swine model, simulating a severe injury by cutting the femoral artery and vein—a scenario that mimics life-threatening bleeding in humans. When injected, the aerogel quickly expands, applying pressure to the wound and creating a physical barrier to stop the bleeding. Its porous structure absorbs blood and traps red blood cells and platelets, accelerating clot formation. The results were interesting: all animals treated with this material survived, and bleeding was controlled faster than existing methods.
This technology is not just about stopping bleeding—it is about saving lives in the most critical moments. It is designed for use by first responders, military medics, and emergency teams, providing a simple yet powerful tool to stabilize patients before they reach the hospital.
Follow the Topic
-
Nature Communications

An open access, multidisciplinary journal dedicated to publishing high-quality research in all areas of the biological, health, physical, chemical and Earth sciences.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Women's Health
Publishing Model: Hybrid
Deadline: Ongoing
Advances in neurodegenerative diseases
Publishing Model: Hybrid
Deadline: Mar 24, 2026