A therapeutic approach to pantothenate kinase associated neurodegeneration
Published in Biomedical Research
Explore the Research
s13023-024-03453-x?utm_campaign=related_content&utm_source=HEALTH&utm_medium=communities
Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation (NBIA) is a group of genetic neurological disorders frequently associated with iron accumulation in the basal nuclei of the brain characterized by progressive spasticity, dystonia, muscle rigidity, neuropsychiatric symptoms, and retinal degeneration or optic nerve atrophy. Pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration (PKAN) is one of the most widespread NBIA disorders. The diagnosis of PKAN is established with clinical features and the "eye of the tiger" sign identified on brain MRI and the identification of biallelic pantothenate kinase 2 (PANK2) pathogenic variants on molecular genetic testing. PANK2 catalyzes the first reaction of coenzyme A (CoA) biosynthesis, thus, altered PANK2 activity is expected to induce CoA deficiency as well as low levels of essential metabolic intermediates such as 4'-phosphopantetheine which is a necessary cofactor for critical proteins involved in cytosolic and mitochondrial pathways such as fatty acid biosynthesis, mitochondrial respiratory complex I assembly and lysine and tetrahydrofolate metabolism, among other metabolic processes.
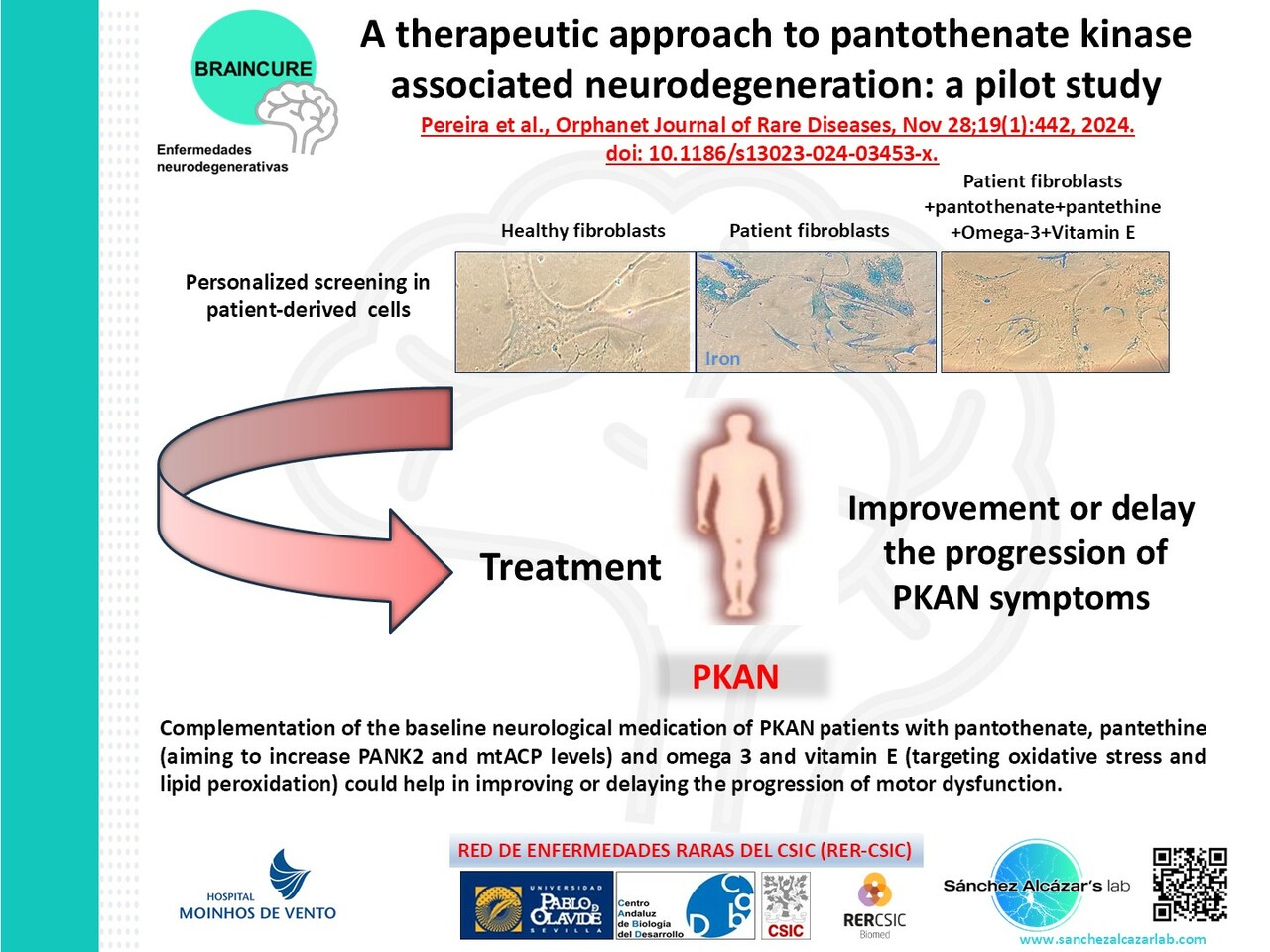
In this work, we examined the effect of a multitarget complex supplements (pantothenate, pantethine, omega-3 and vitamin E) on in vitro patient-derived cellular models and the clinical outcome of the adjuvant supplements in combination with the baseline neurological medication in three PKAN patients.
Results: Multitarget complex supplements significantly reduced iron accumulation and increased PANK2 and ACP expression levels in the cellular models derived from all three PKAN patients. In addition, the adjunct treatment to the standard neurological medication improved or stabilized the clinical symptoms of patients.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that multitarget complex supplements can be clinically useful as augmentation therapy for PKAN patients harboring pathogenic variants with residual enzyme levels.
Authors:
Follow the Topic
-
Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases

An open access, peer-reviewed journal that encompasses all aspects of rare diseases and orphan drugs and publishes high-quality reviews on specific rare diseases.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Advances in Our Understanding of Glutamatergic Receptor Biology: Selected Papers from the 7th European GRIN Conference
This Collection showcases selected research presented at the 7th European GRIN Conference, where families, clinicians, and scientists gathered to explore the latest discoveries in GRI disorders.
The featured papers delve into the biology of NMDA and AMPA receptors, their gene variants, and their clinical implications, offering insights into complex symptomatology and emerging therapeutic approaches.
Reflecting the collaborative and translational nature of the event, this Collection bridges foundational science with real-world impact, aiming to improve outcomes for individuals affected by GRI-related conditions.
All submissions in this collection undergo the journal’s standard peer review process. Similarly, all manuscripts authored by a Guest Editor(s) will be handled by the Editor-in-Chief. As an open access publication, this journal levies an article processing fee (details here). We recognize that many key stakeholders may not have access to such resources and are committed to supporting participation in this issue wherever resources are a barrier. For more information about what support may be available, please visit OA funding and support, or email OAfundingpolicy@springernature.com or the Editor-in-Chief.
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Jun 15, 2026
Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in
In this manuscript we provide evidence that the complementation of the baseline neurological medication of PKAN patients with pantothenate, pantethine (aiming to increase PANK2 and mtACP levels) and omega 3 and vitamin E (targeting oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation) could help in improving or delaying the progression of motor dysfunction. Novel targeted treatments are extremely needed to retard or stop disease progression and to optimize the quality of life in PKAN.