Discovery of Easy Activity Promotion of Photoelectrochemical Reactors: Time & Energy Saving via Coupled Faradaic/Electrostatic Boosting Strategy!
Published in Chemistry and Earth & Environment
Because of emerging widespread applications in various fields, including water quality, energy & fuel production and environmental remediation issues, it is crucial to introduce a facile cost-effective route to enhance the activity of these PEC reactors, reduce their operational time and save their energy/power consumption.
Through the facile Coupled Faradic/Electrostatic Strategy and employing an electrostatic bias to the photoelectrode (Fig. 1), the activity of PEC reactors can be substantially boosted, and their operational time and electrical consumption can be decreased by almost half!
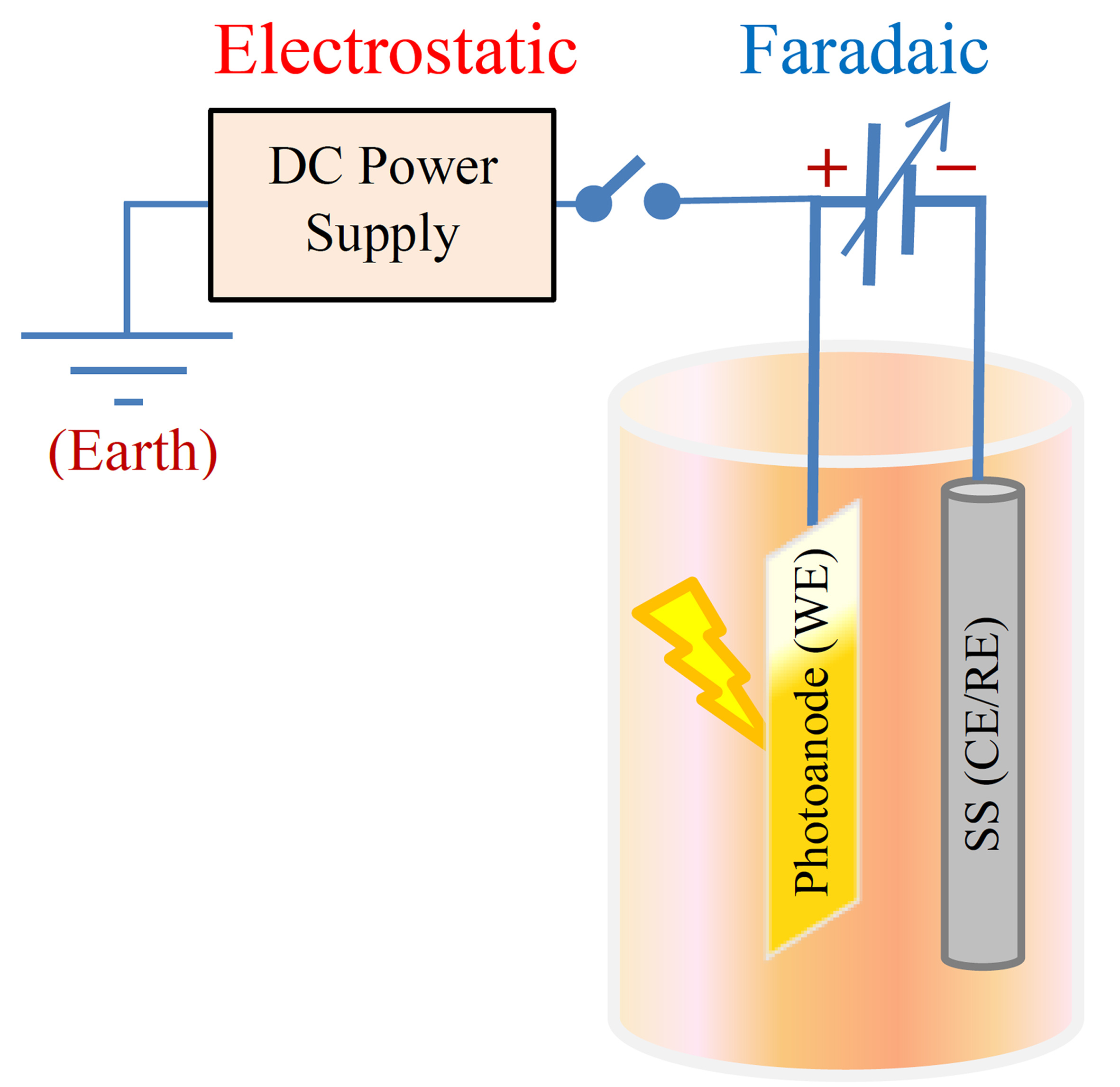
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the dually-biased photoelectrochemical (PEC) reactor with the manner of applying non-faradaic (electrostatic) and faradaic potential biases to the photo-reactor [Source: Journal of Power Sources 602 (2024) 234329; https://authors.elsevier.com/a/1im4f1M7w0emdr].
Although the strategy mentioned above has been originally suggested to boost the activity of a given PEC reactor for dye degradation, it is predicted it can be easily extended to other PEC systems including water splitting, solar-to-fuel conversion, artificial photoelectrochemical synthesis, etc.
Other related source: npj Clean Water (2023) 6:10 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41545-023-00230-4
Follow the Topic
-
npj Clean Water

This journal publishes high-quality papers which report cutting-edge science, technology, application, policy and societal issues that contribute towards a more sustainable supply of clean water.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Advancing Artificial Intelligence Innovations for Resilient and Sustainable Clean Water: Novel Methodologies and Case Studies
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Feb 28, 2026
Advances in Smart Water Systems: From Source to Tap and Beyond
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Feb 28, 2026




Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in