From a mother's hands to a deep understanding—preserving Algerian culinary heritage
Published in Social Sciences and Agricultural & Food Science
Explore the Research
Production process, rheology, and sensory characterization of Algerian porridge and flatbread derived from Arum italicum tubers
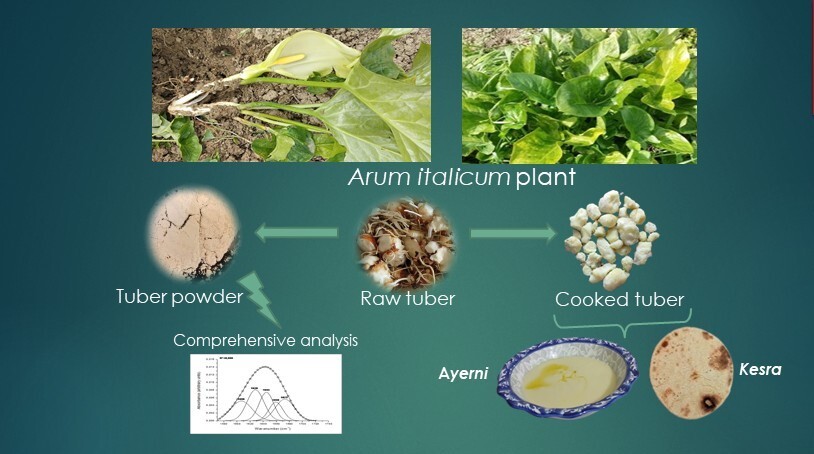
The scientific study began not in a laboratory environment, but in a kitchen. By observing a mother from a mountainous area of Algeria preparing traditional porridge and flatbread made from Arum italicum tubers, just as her ancestors did before her. Her desire to preserve and promote this knowledge truly motivated this research. She continues to practice this ancestral method today, even though such traditions are rapidly fading among the younger generations.
Inspired by her commitment, we decided to record and scientifically study these traditional practices—not only with the aim of preserving culinary heritage but also to examine their nutritional and functional potential. Our work included both field surveys and laboratory studies. The research conducted allowed us to establish the traditional diagrams for the preparation of Kesra (flatbread) and Ayerni (porridge), while the scientific study focused on the physicochemical and structural properties of the tuber powders, as well as the rheological and sensory analysis of the two products made from the Arum italicum tuber.
Tubers with remarkable nutritional and functional properties
The results corroborated what local experts had already suggested: these tubers have a high energy value (366.88 kcal/100 g) and are extremely rich in carbohydrates (80.86%), exhibiting a remarkable water-retention capacity and outstanding solubility. The FT-IR analysis revealed a predominantly β-sheet structure, indicating a high-value starch composition. Rheological examinations have demonstrated that the consistency of the porridge was more uniform, while sensory analysis indicated that both products were equally well-received by the new generation.
Traditional products are made from a dough derived from tubers that have been previously boiled and steamed repeatedly to eliminate their toxicity related to the presence of alkaloids and calcium oxalate crystals. The cooking methods practiced by previous generations can eliminate the toxicity of the tubers. If this method has been passed down orally by previous generations, scientific results have validated its effectiveness, thereby reinforcing the relevance of this ancestral knowledge.
Three strategic areas of enhancement.
The exploitation of Arum italicum tubers is part of a sustainable and local development perspective, addressing three fundamental challenges:
- Highlighting Algerian culinary heritage through the development of healthy products inspired by traditions.
- Establishment of economic opportunities by facilitating the integration of natural and accessible raw materials into new commercial circuits.
- Promotion of local agroecological practices by supporting small producers and strengthening the resilience of food systems.
This article goes beyond the scope of a simple scientific report—it pays homage to a mother's knowledge, highlights the importance of oral traditions, and underscores the crucial role of women as preservers of culinary heritage. By recording these traditions and confirming their nutritional value, our goal is to contribute to food sustainability while honoring the wisdom passed down through generations.
Follow the Topic
-
Discover Food

This is a transdisciplinary, open access journal that provides a leading platform for the rapid dissemination of knowledge and advances covering the research and innovation that is taking place across the food sector.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Emerging Trends in Fermented Dairy and Non-Dairy Products: Fermentation Technologies, Innovations, and Health Benefits
Fermented dairy and non-dairy products have garnered significant attention in recent years due to their perceived health benefits, diverse flavors, and nutritional profiles. This collection explores the latest trends and advancements in these fermented products, focusing on fermentation technologies, innovations, and their potential health benefits.
The collection delves into the evolving landscape of fermentation technologies applied to both dairy and non-dairy substrates. It examines innovative techniques and methodologies aimed at enhancing product quality, flavor development, and nutritional content. Topics include novel microbial cultures, fermentation conditions optimization, and the integration of advanced processing technologies.
Scientific insights into the health-promoting properties of fermented dairy and non-dairy products are a central theme. Contributors explore the role of probiotics, prebiotics, and bioactive compounds generated during fermentation in supporting digestive health, immune function, and overall well-being. Discussions encompass the impact of fermentation on nutrient bioavailability and the potential therapeutic applications of fermented products.
Drawing from diverse disciplines such as food science, microbiology, and nutrition, this collection bridges scientific research with practical applications. It fosters cross-disciplinary dialogue on fermentation technologies, innovations, and their implications for public health and sustainable food systems. This collection is designed for researchers, industry professionals, policymakers, and educators interested in the latest developments and future directions of fermented dairy and non-dairy products. It serves as a comprehensive resource for understanding the scientific underpinnings, technological advancements, and market dynamics shaping this rapidly evolving field.
Keywords: Fermentation technologies; dairy and non-dairy products; Probiotics; Prebiotics; Bioactive compounds; Microbial cultures; functional properties; health benefits
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Feb 28, 2026
How Can Active and Smart Packaging Help Shape the Future of Food Preservation: Challenges and Alternatives
Active and smart food packaging can be defined as systems that provide a positive interaction between the food and the packaging. While active packaging directly interacts with the packaged food through the absorption of substances produced by the packaged food, or emission of active compounds, such as antimicrobial or antioxidant agents, the smart or intelligent packaging provide real-time information about the foods’ conditions, such as temperature fluctuations. Both these types of food packaging have the main goal to avoid food waste, improving foods’ quality and safety.
The goal of this Topical Collection is to address the challenges of development and producing these types of packaging, considering a sustainable approach, that also promotes a circular economy.
Keywords:
Food preservation; Shelf-life; Circular economy; Food waste; Food additives; Phenolic compounds
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Jun 30, 2026





Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in