Generation of Precision Reconfigurable Micromolds for High-Resolution Polymer Replication
Published in Materials
Micromolds are widely used for polymer replication to fabricate all kinds of microstructured surfaces - ranging from surfaces with anisotropic wetting properties or self-cleaning capabilities to high precision products like microfluidic devices and microoptics. Due to the high demand for micromolds, a variety of technologies has been developed such as photolithography, micro-milling or laser cutting. The essence of these methods is to remove a portion of the material to create a mold as in photolithographic etching, micro-milling and laser ablation techniques. However, such technologies often require harmful solutions, produce considerable waste during the structuring process, and are completely static and cannot be changed.
Previous research has shown that photo-responsive hydrogels can change their volume via absorbing or expelling water when stimulated with light. This way, hydrogels can be selectively shaped by light through a reversible swelling/deswelling process. Therefore, we reasoned that if a high resolution is achieved, a reconfigurable micromold can be generated on a photoswitchable hydrogel surface. This would be a versatile tool for creating reusable and re-writable molds for microfluidics and microoptics at minimal requirements for materials and equipment.
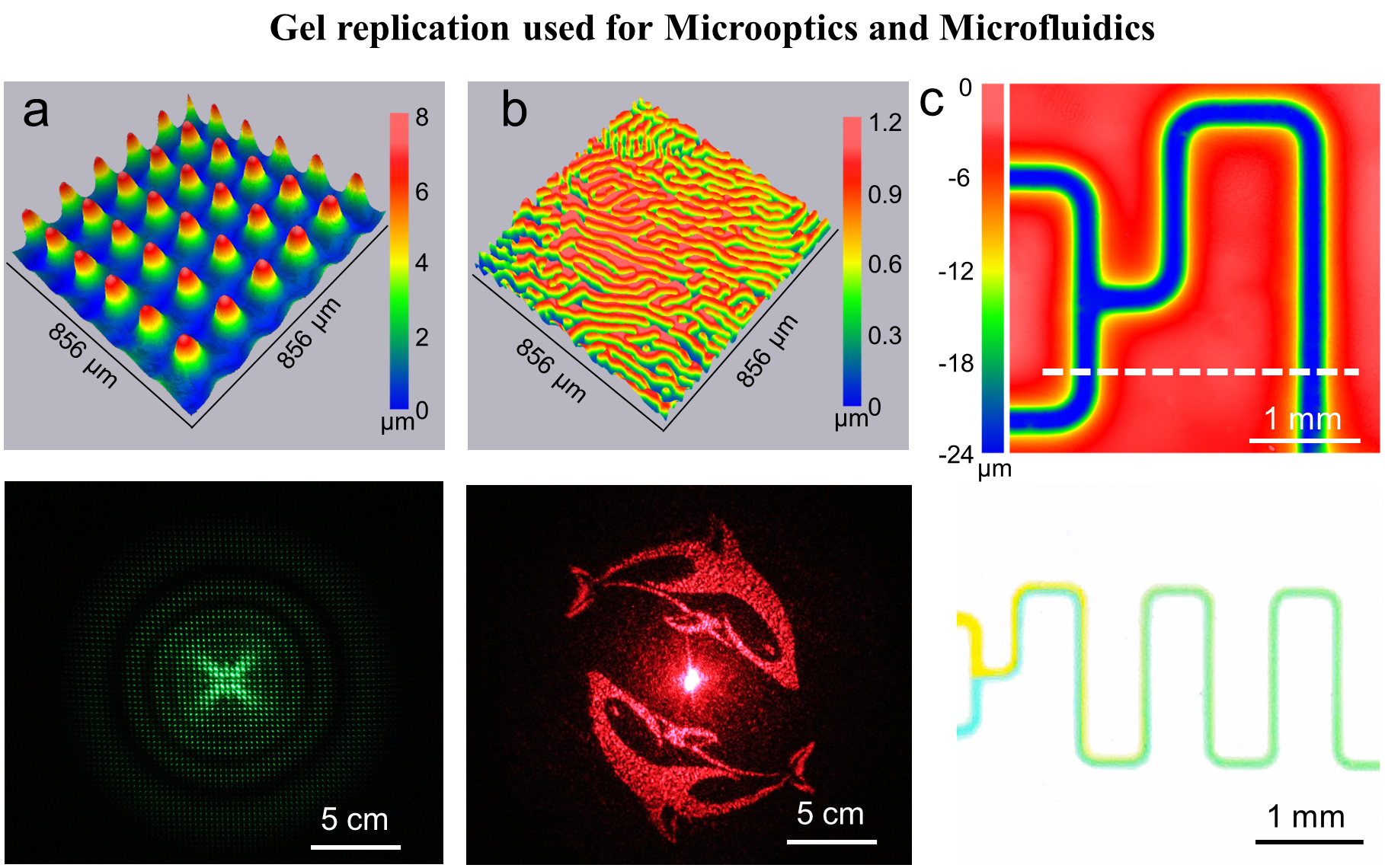
To achieve the formation of a suitable gel we synthesize a photo responsive hydrogel utilizing host-guest interaction between α-cyclodextrin molecules and azobenzene groups. Using a physical mask with micropatterns, the hydrogel shrinks locally under illumination resulting in microstructures on the hydrogel surface. The fabricated micromolds demonstrate a high resolution down to 30 µm. In addition, the reversible nature of the gels allows micromolds to be structured, reset and structured again using different patterns to generate a different micromold – making this method highly versatile and material-efficient. We also demonstrate that physical masks are not necessarily required, and that micromolds with the same performance can be prepared via maskless lithography using a digital micromirror device (DMD). An attractive advantage of this digitalized lithography is that the micromolds with complex gradient height distribution can be generated within one single exposure.
Our micromolds achieve high fidelity and high surface smoothness, leading to high-quality PDMS replicas with an Ra of 2.68 nm and Rq of 3.4 nm. Using our methods, we produced precision products including a microlens array, diffractive optical elements and a microfluidic mixer structure with 100 µm width microchannels. This technology provides access to a simple method for the fabrication of reusable micromolds for polymer structuring and enables the generation of high-quality molds with minimal equipment and resources.
For more details, check out our paper “link: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-50008-6” on Nature Communications.
This post is contributed by Pang Zhu and Dorothea Helmer.
Follow the Topic
-
Nature Communications

An open access, multidisciplinary journal dedicated to publishing high-quality research in all areas of the biological, health, physical, chemical and Earth sciences.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Women's Health
Publishing Model: Hybrid
Deadline: Ongoing
Advances in neurodegenerative diseases
Publishing Model: Hybrid
Deadline: Mar 24, 2026






Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in