Harnessing rice husk ash for sustainable construction: a comprehensive review of challenges, opportunities, and future perspectives
Published in Earth & Environment, Materials, and Sustainability

Our paper examines the potential of rice husk ash (RHA) as a sustainable construction material. RHA, derived from burning rice husk, is rich in amorphous silica and offers environmental and economic benefits. However, its use is limited by processing challenges and a lack of understanding of its properties. We review RHA production technologies, its properties, and its impact on concrete's mechanical properties, durability, and permeability. Key factors like burning temperature and pretreatment techniques significantly influence RHA performance. Incorporating 10–20% RHA can enhance concrete strength. Read the full paper here.
Follow the Topic
-
Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management

This journal specializes in the interdisciplinary science of material cycles and waste management.
What are SDG Topics?
An introduction to Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Topics and their role in highlighting sustainable development research.
Continue reading announcement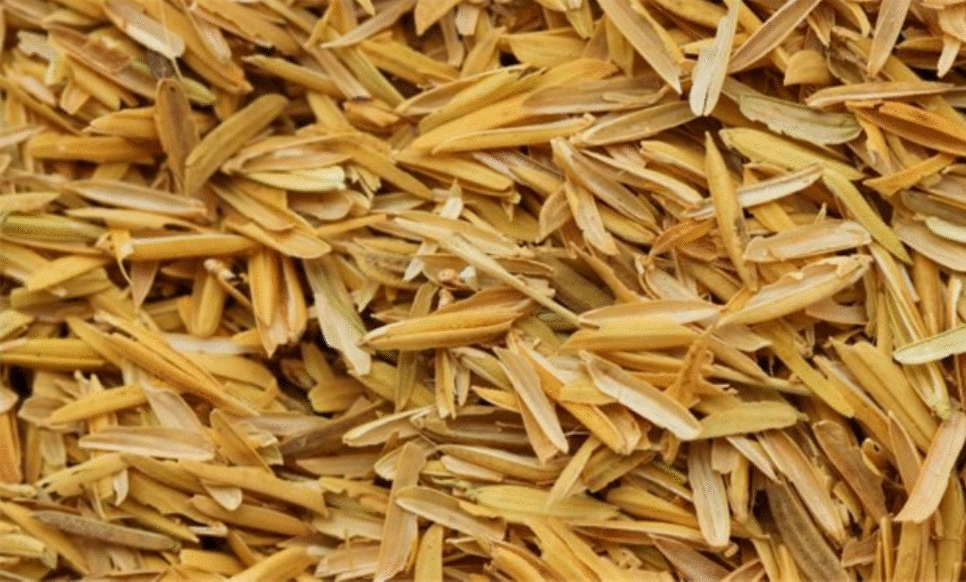

Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in
Después de los procesos de selección de la cáscara de arroz, incineración, molienda y tamizado de la ceniza, es necesario someterlo a un análisis por fluorescencia de rayos X para comprobar su composición y poder utilizarla como material cementante.
After the processes of selecting the rice husks, incineration, grinding, and sifting the ash, it is necessary to subject it to X-ray fluorescence analysis to check its composition and ensure it can be used as a cementing material.