Integrated metagenomics identifies a crucial role for trimethylamine-producing Lachnoclostridium in promoting atherosclerosis
Published in Microbiology

Numerous studies on intestinal microbiota over the past ten years have confirmed their pivotal roles in human health and diseases, including cardiovascular diseases1,2,3. Recently, the gut microbiota as a whole, has recently been found to be an important contributor to the progression of cardiovascular diseases1,4,5. Plasma trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO) has been confirmed as an independent risk factor for atherosclerosis, thrombus formation6, and myocardial infarction5,7. Trimethylamine (TMA), a precursor of TMAO, is a small molecular weight byproduct of intestinal microbial metabolism of dietary choline, carnitine, and phosphatidylcholines8,9,10and converted to trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO) in the liver via flavin-containing monooxygenase 311,12.
In our work, using an integrated metagenomic approach, we analyzed reference genomes from the three reference resources, 12 metagenomic datasets from public metagenomic databases and biologically validated our findings with an Apoe−/− mice model. We sought to investigate: (1) the bacteria in the human gut microbiota that encode TMA-lyase in their genomes (2) the abundances and activities of these TMA-producing bacteria in the gut and (3) whether or not the TMA-producing bacteria increase the risk of developing atherosclerosis.
The gut microbiota is known to convert carnitine, betaine, and choline to TMA by utilizing three TMA-lyase complexes, cntA/B, yeaW/X, and cutC/D, respectively. We identified the TMA-lyase sequences of the TMA-producing bacteria based on the three reference genomic resources. The final 885 TMA-lyase reference sequences were identified from three resources, 451 from the Human Microbiome Project database, 216 from the Unified Human Gastrointestinal Genome, and 218 reference sequences from 4930 species-level genome bins by taking the initial 983 sequences as query. In order to achieve the representing TMA-producing bacteria, we applied an integrated reference metagenomic sequence dataset was acquired from several public cohorts (Fig. 2).
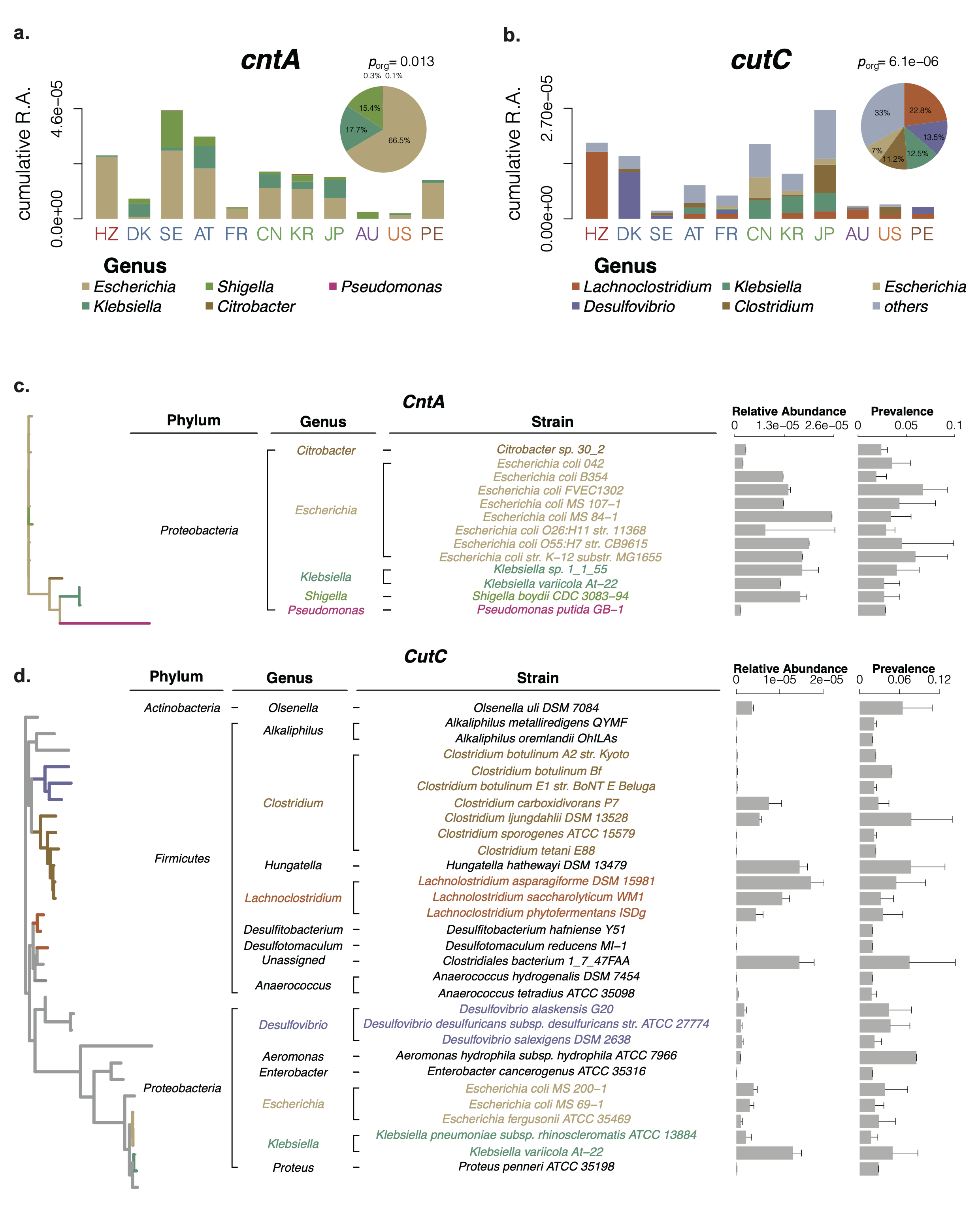
Fig. 2: Relative abundance distribution and taxonomic identification of cntA and cutC.
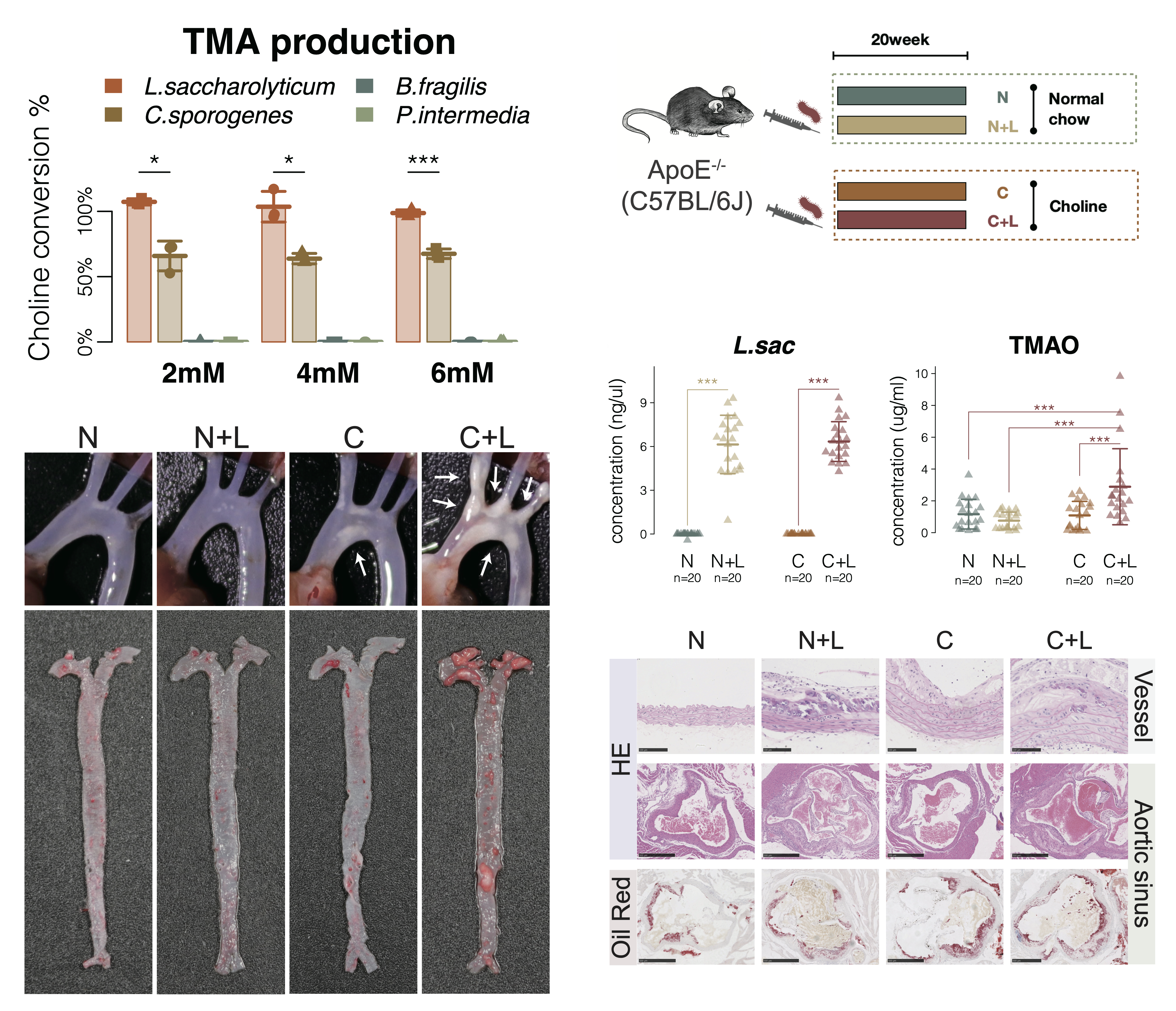
After our taxonomic identification, we unexpectedly found cutC showed significantly increased relative abundance in the patients with atherosclerosis, and the genus Lachnoclostridium, the highest cutC containing genus, were significantly increased in patients with atherosclerosis. As a result, L. saccharolyticum WM1, a representative strain of Lachnoclostridium, effectively converted choline to TMA at a transformation rate near 100%, much higher than 63% for C. sporogenes. This strain was found to elevate serum TMAO and promote the formation of atherosclerosis in ApoE−/− mice when co-administered with choline.
Follow the Topic
-
npj Biofilms and Microbiomes

The aim of this journal is to serve as a comprehensive platform to promote biofilms and microbiomes research across a wide spectrum of scientific disciplines.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Natural bioactives, Gut microbiome, and human metabolism
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: May 20, 2026
Harnessing plant microbiomes to improve performance and mechanistic understanding
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Jun 01, 2026



Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in