Melatonin inhibits bladder tumorigenesis by suppressing PPARγ/ENO1-mediated glycolysis
Published in Cancer
Bladder cancer (BLCA) is a common and deadly cancer that starts in the bladder lining. It’s one of the top ten cancers worldwide. In 2022, there were approximately 91,893 new cases in China and 84,825 in the U.S., making it the second most common urinary system cancer [1]. It mainly affects people aged 50 to 70 and is more common in men than women. Recently, the number of new cases and deaths from BLCA has been increasing.
Treatment for BLCA has evolved from just surgery and chemotherapy to include radiotherapy and immunotherapy. However, resistance to drugs like cisplatin and gemcitabine is a major challenge, highlighting the need for research into overcoming this resistance [2].
Melatonin, a natural hormone known for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, also shows potential in cancer treatment. Studies have shown that melatonin can enhance the effectiveness of existing cancer drugs in various cancers by affecting different cellular mechanisms [3]. However, its effects on BLCA have not been studied much.
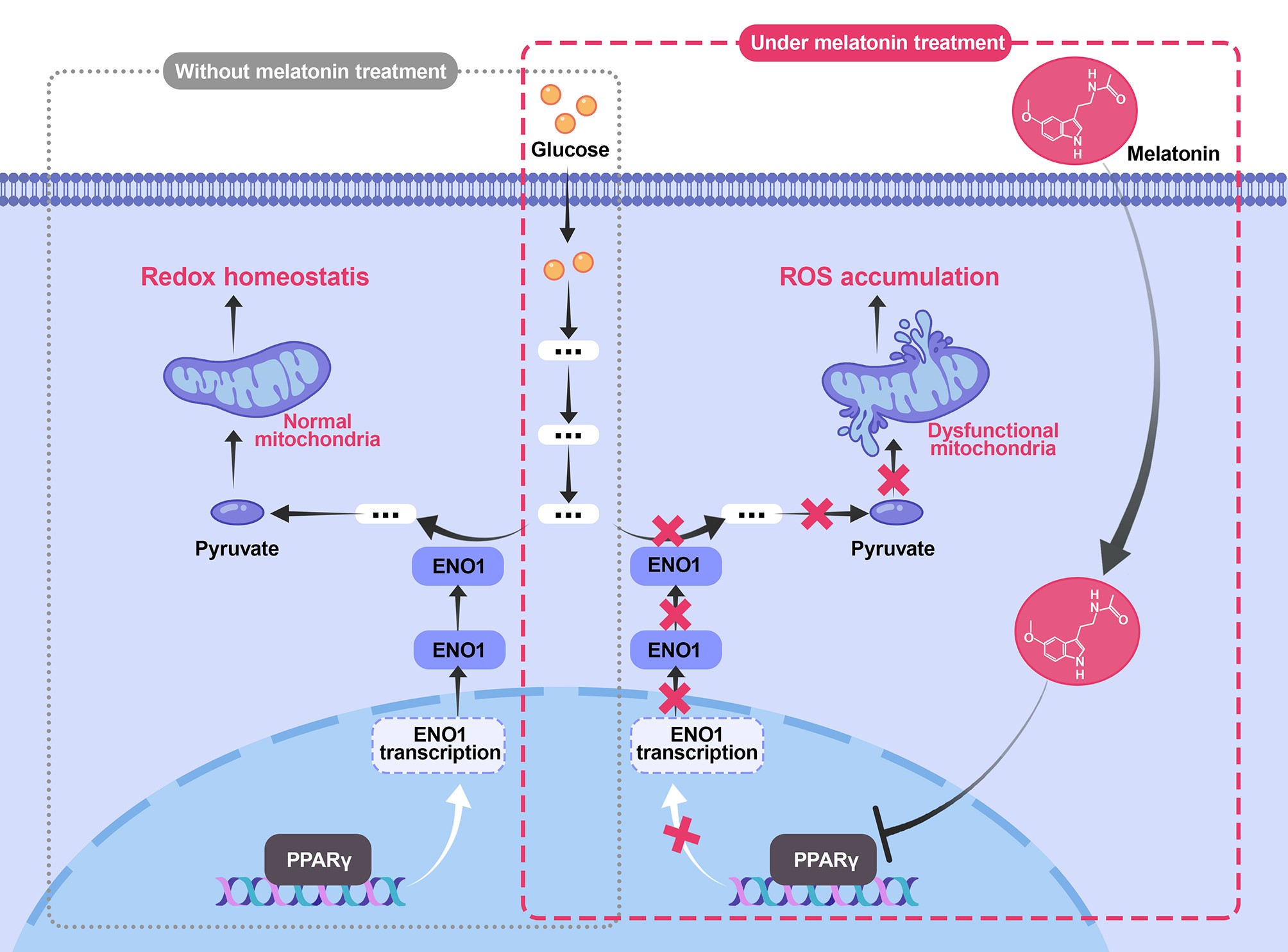
Our research focused on how melatonin can help treat BLCA. We found that melatonin can disrupt BLCA cell metabolism, particularly glycolysis (the process cancer cells use to generate energy), by targeting specific molecular pathways and increasing reactive oxygen species, which disrupt cell function. This disruption enhances the effectiveness of the chemotherapy drug gemcitabine against BLCA cells.
Overall, our study suggests that melatonin could be a valuable addition to BLCA treatment by reprogramming cancer cell metabolism and improving drug response.
References
[1] Siegel RL, et al. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin 2022, 72(1): 7-33.
[2] Stenzl A, et al. Treatment of muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder cancer: update of the EAU guidelines. Eur Urol 2011, 59(6): 1009-1018.
[3] Shen D, et al. The inhibitory effect of melatonin on human prostate cancer. Cell Commun Signal 2021, 19(1): 34.
Follow the Topic
-
Cell Death & Disease

This journal seeks to encompass the breadth of translational implications of cell death and promote diverse and integrated areas of experimental and internal medicine with its specialties, including cancer, immunity and neuroscience.
Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in