YKT6 drives bladder cancer progression by stabilizing β-catenin via a USP7-mediated mechanism
Published in Cancer and Cell & Molecular Biology
While YKT6 is canonically known for mediating intracellular membrane fusion and vesicular transit, its specific function in BLCA tumorigenesis has remained elusive. Our analysis of public datasets and clinical tissue microarrays demonstrates that YKT6 is significantly upregulated in BLCA tissues compared to normal counterparts. Furthermore, we observed that elevated YKT6 expression correlates strongly with advanced tumor grade, aggressive histology, and poor patient prognosis.
To determine the biological impact of this upregulation, we conducted functional analyses which revealed that YKT6 promotes BLCA cell proliferation, migration, and metastasis both in vitro and in vivo.
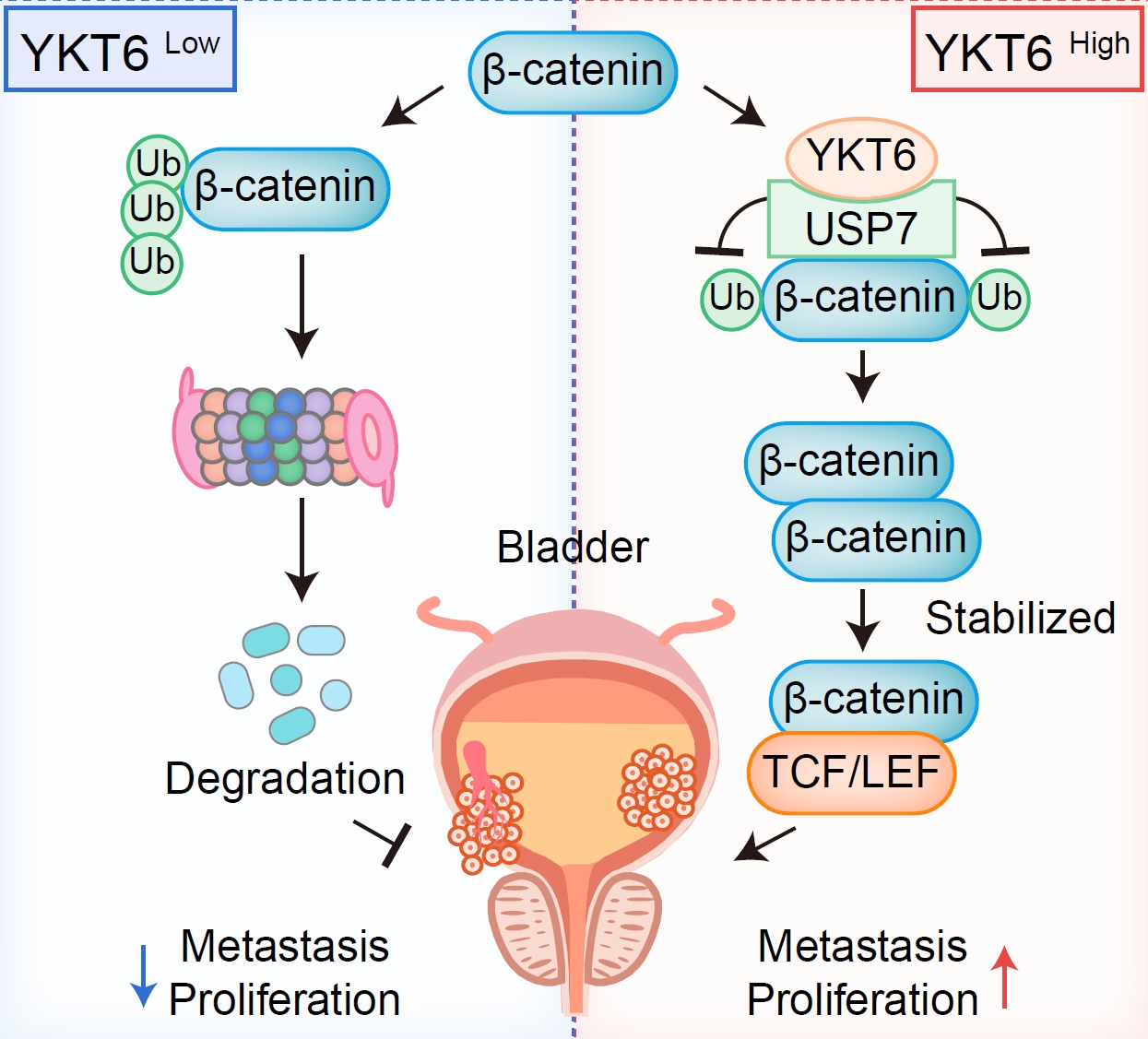
In this study, we further explored the molecular mechanism driving these malignant phenotypes. We identified a novel signaling axis in which YKT6 activates the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Specifically, as shown in the Figure above, YKT6 acts as a scaffold to recruit the deubiquitinase USP7. This interaction facilitates the deubiquitination of β-catenin, thereby inhibiting its proteasomal degradation. The resulting stabilization leads to the nuclear accumulation of β-catenin, which subsequently induces the expression of oncogenic target genes and drives epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT).
Finally, we demonstrated that the YKT6/USP7/β-catenin axis is a viable therapeutic target. Pharmacological inhibition of USP7 was sufficient to abrogate YKT6-mediated β-catenin stabilization and reverse tumor progression. Overall, our study unveils YKT6 as a critical promoter of BLCA and suggests that targeting the YKT6-USP7 interaction offers a promising avenue for precision therapy.
Reference:
[1] Tu S, Du W, Luo Y, Shi J, Liu T, Ji M, Xiong K, Chen S, Zhou F, Li M, Yu J, Wang G, Ju L, Zhang Y, Xiao Y, Wang X, Qian K. YKT6 Promotes Bladder Cancer Progression by Stabilizing β-catenin Through USP7-Mediated Deubiquitination. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Nov 26: e07166. doi: 10.1002/advs.202507166.

Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in