Mountain chickadees are flexible in their breeding timing - but early breeding is best
Published in Ecology & Evolution and Zoology & Veterinary Science
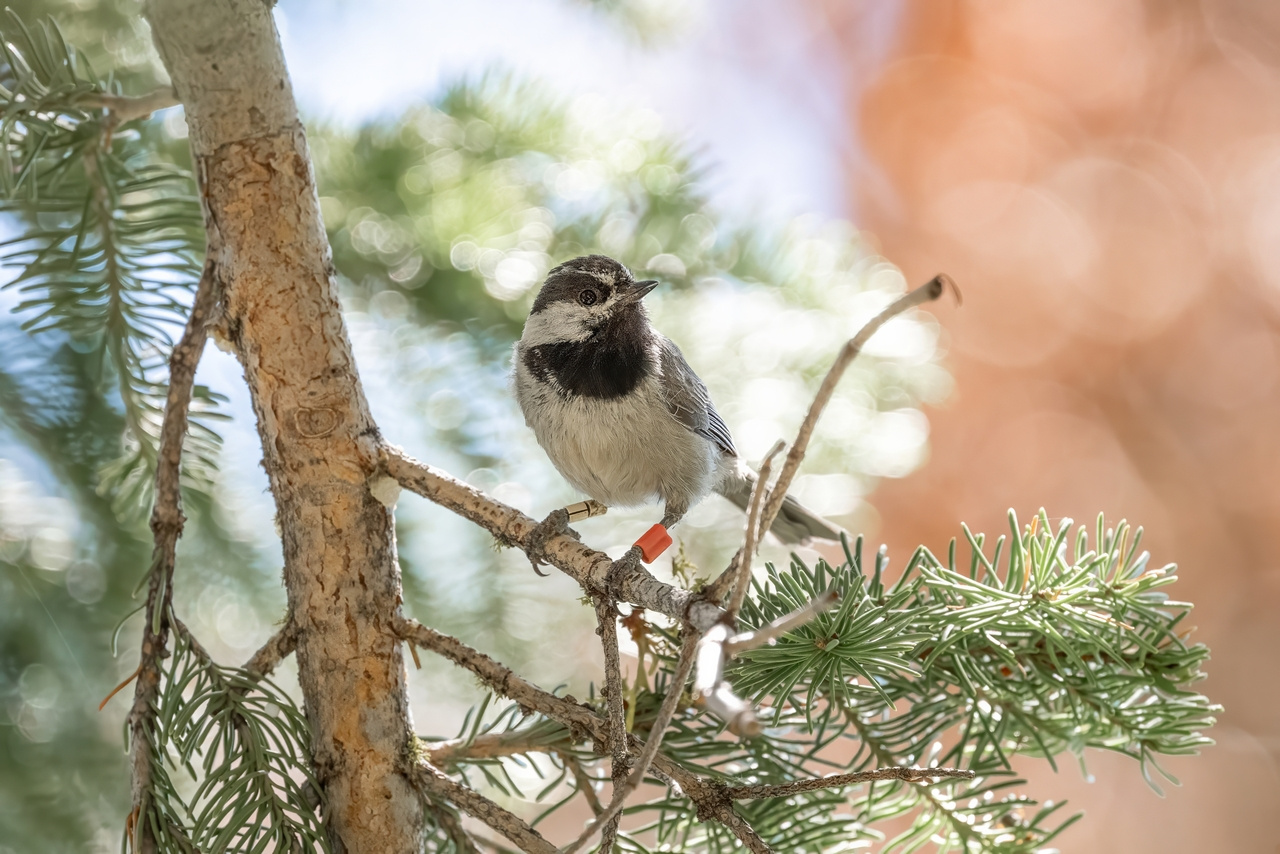

Setting the Scene

It is late June of 2023 and I am snowshoeing my way up to check nest boxes in the Tahoe National Forest, California, USA. I am a PhD student in Dr. Vladimir Pravosudov's Cognitive and Behavioral Ecology Lab at the University of Nevada, Reno, where our lab has an established long-term mountain chickadee (Poecile gambeli) study system. Dr. Pravosudov began collecting data on chickadees breeding in some 300+ nest boxes in 2013. Each year has been different than the last, sometimes in logistically challenging ways, like when there are still 1-2 meters of snow on the ground in the middle of the summer. The Sierra Nevada mountains where our field site is located are known for extreme snowpack - sometimes reaching 6 meters in higher elevation locations - but also for extreme drought. This year-to-year environmental variation can heavily impact the animal populations that call these mountains home. Chickadees are no exception.

Mountain chickadees are small non-migratory songbirds native to Western North America. They specialize in caching tens of thousands of conifer seeds every autumn and rely on their food caches to survive harsh winters. When the summer rolls around, they must time their reproduction so that the young hatch during a period of adequate insect food availability, but waiting until the food reaches a seasonal peak may be disadvantageous. This is because after the young fledge, they must molt, join a social flock, and cache enough food to survive the winter, all of which takes time. Additionally, during particularly heavy snow years, chickadees may not be able to access nest cavities or nesting materials until much later in the season, creating physical limitations to breeding timing.
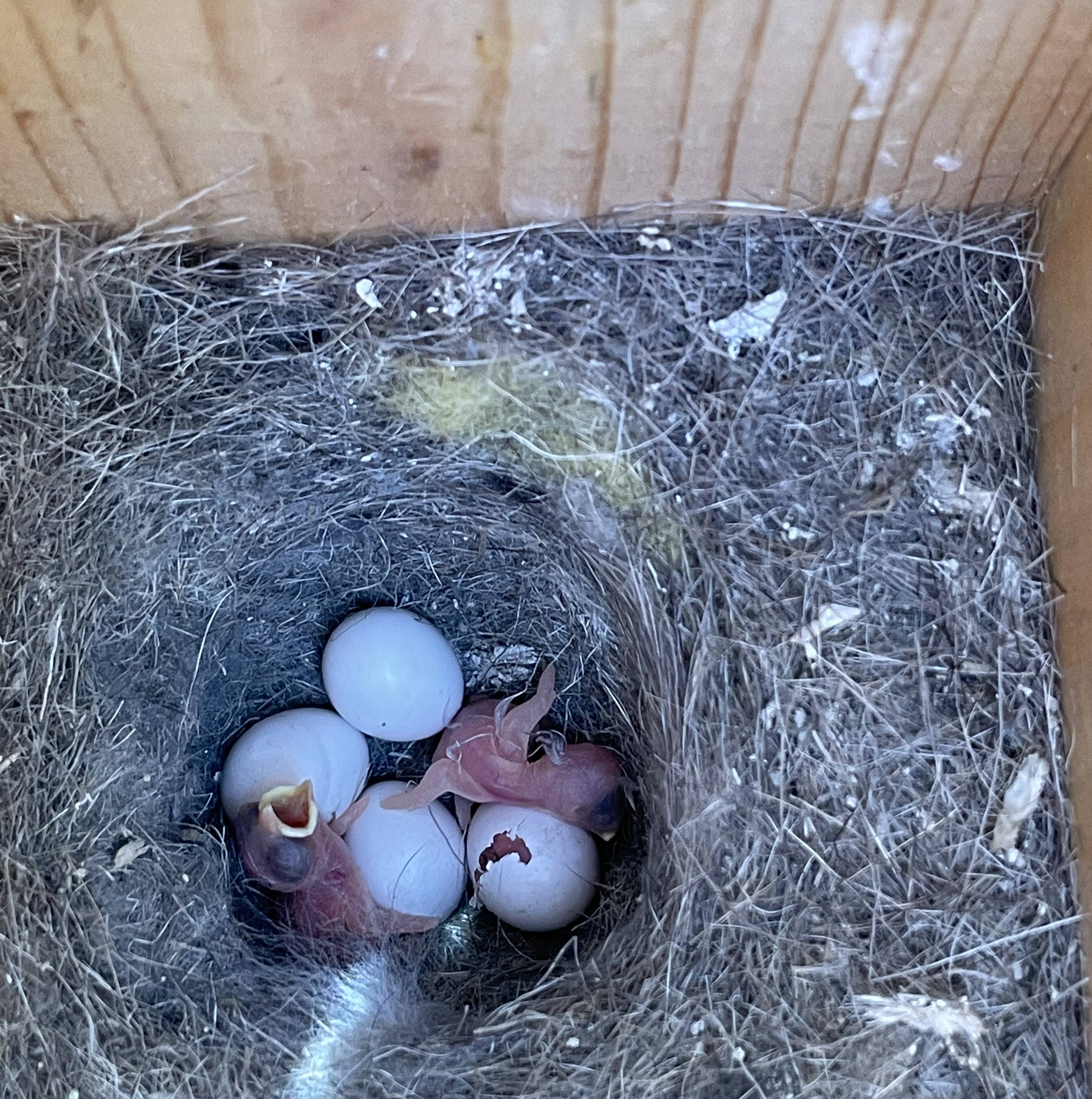

Tracking Birds Across Years
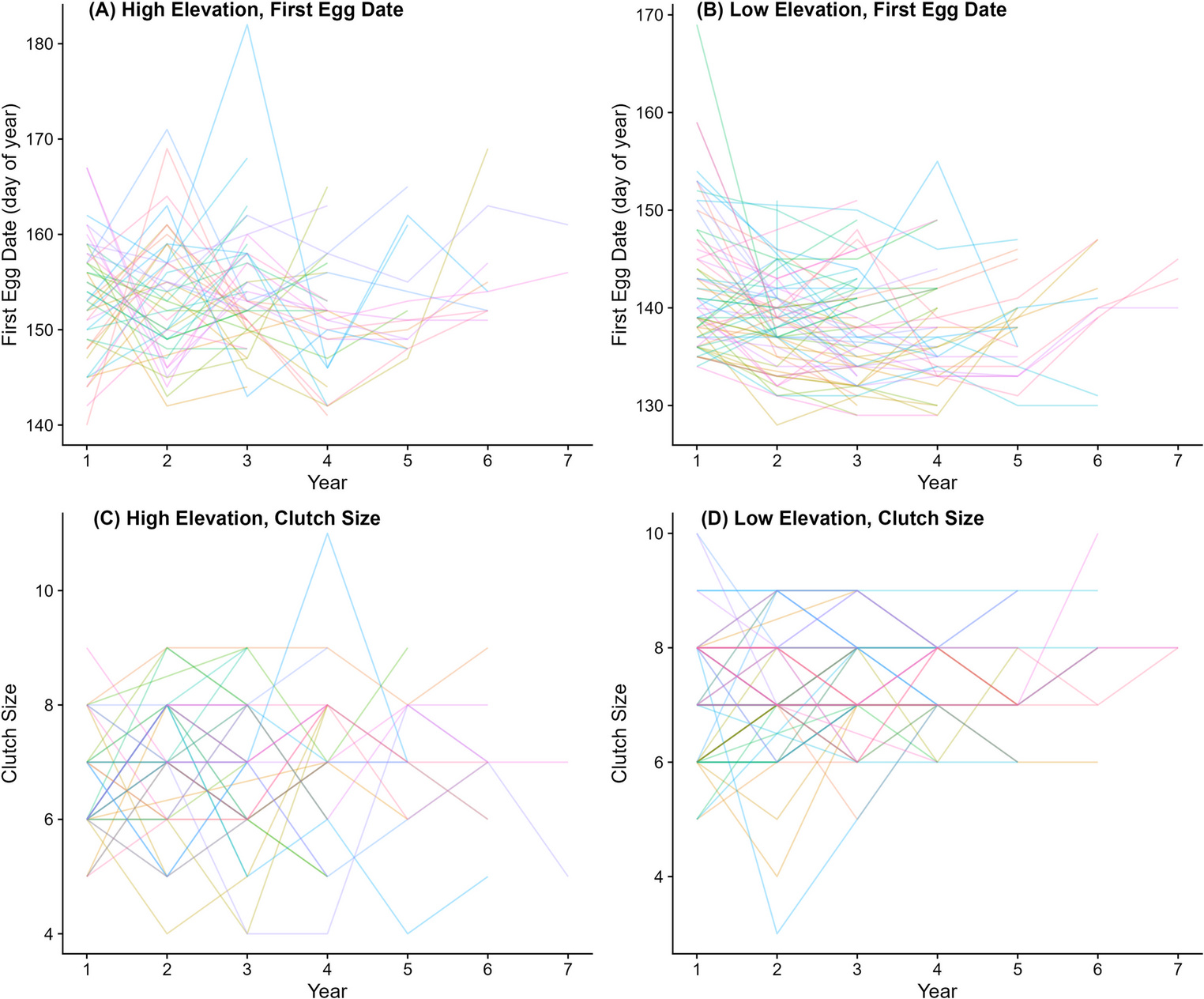
Because chickadees are highly resident and do not disperse far from their natal sites, individuals are easy to track over time. All birds in our system are tagged with a unique combination of color bands, allowing us to resight individuals easily. In this study, we tracked 109 individual female birds that bred 3 or more years in nest boxes in our system from 2013-2023. With these data, we were able to calculate how flexible each female was in her breeding timing (lay date) in response to spring temperature and winter snow accumulation. We also measured repeatability in lay dates and clutch sizes.
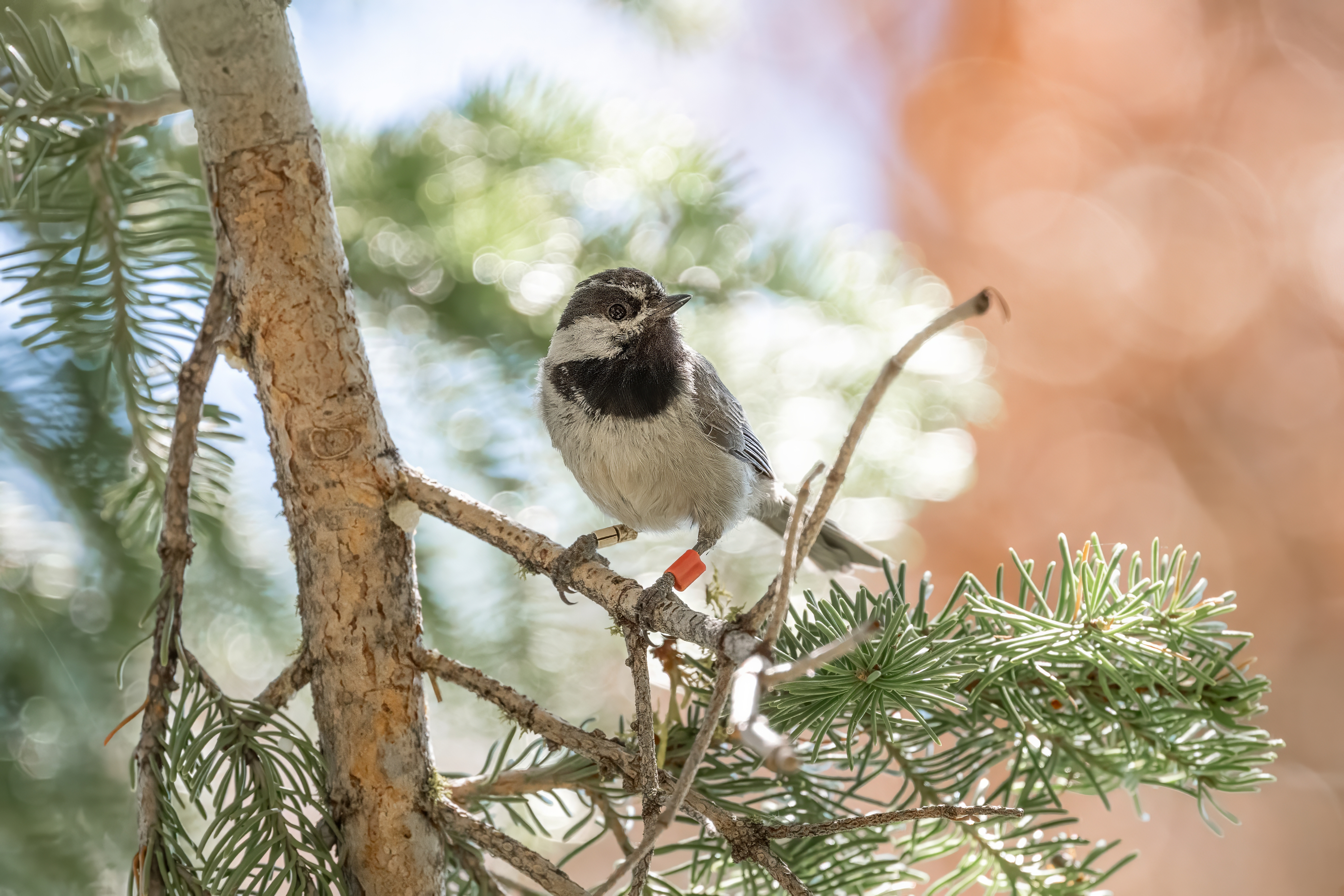

Due to extreme annual swings in snow pack, particularly at higher elevations, we hypothesized that mountain chickadees that were more flexible in their reproductive timing (i.e., bred earlier during low snow years and later during heavy snow years) would have higher reproductive success. We also tested whether chickadees adjusted their breeding timing to spring temperatures and whether individuals that showed higher flexibility had higher reproductive success. To measure reproductive success, we calculated the total number of fledglings produced, the average relative clutch size (how much an individual deviated from the annual population mean), and the average relative brood size.
Our Key Findings
We discovered that both lay dates and clutch sizes were repeatable within individual females. However, we also found that female mountain chickadees showed flexibility in breeding timing - and the degree of flexibility differed among individuals. Some individuals seemed to breed around the same time each year, but others shifted their lay dates much more in response to climate. However, we found no strong evidence that individuals that were more or less flexible in their breeding timing had higher reproductive fitness. Instead, we observed that birds are experiencing selection for earlier breeding in this system (associated with larger average relative clutch and brood sizes).
Flexibility in breeding timing is an important behavioral trait, and even if the degree of flexibility is not currently under selection, this does not mean that selection will not act in the future. With accelerating environmental variability and warming temperatures associated with climate change, chickadees of the future may experience different selection pressures. Additionally, the fact that we found variation in individual flexible responses suggests that flexibility in breeding timing could be a trait that may undergo selection, given that it has a heritable component.
Read our full paper here: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00265-025-03629-w
Follow the Topic
-
Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology

This journal publishes reviews, original contributions and commentaries dealing with quantitative empirical and theoretical studies in the analysis of animal behavior at the level of the individual, group, population, community, and species.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Kappeler’s framework for animal social systems and its impact on behavioral ecology and sociobiology
Prof. Dr. Peter M. Kappeler’s seminal work on animal social systems has built a strong conceptual foundation for generations of researchers (Kappeler and van Schaik 2002; Kappeler 2019). One of the most notable and important contributions of his work is a clear framework for animal social systems. This framework emphasizes that there are four inter-related components of the social system: (i) social organization, (ii) social structure, (iii) mating system, and (iv) care system. It is powerful for numerous reasons; one of which is that it clearly defines components that promote empirical and comparative research that does not confuse or confound behaviors that fall under different forms of selection. The framework allows us to identify >1000 types of social systems, resulting in a more comprehensive and holistic study of animal social systems. Consequently, it has enormous potential to shape our understanding of social complexity across a broad range of taxa.
It will also address United Nations Sustainable Development Goals 4: Quality Education, 13: Climate Action and 15: Life on Land.
Pre-submission enquiries are welcome.
Keep up with the latest Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology content by signing up for Journal Alerts today!
Publishing Model: Hybrid
Deadline: Sep 01, 2026



Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in