NPB Editor's Choice
Published in Healthcare & Nursing, Chemistry, and Neuroscience
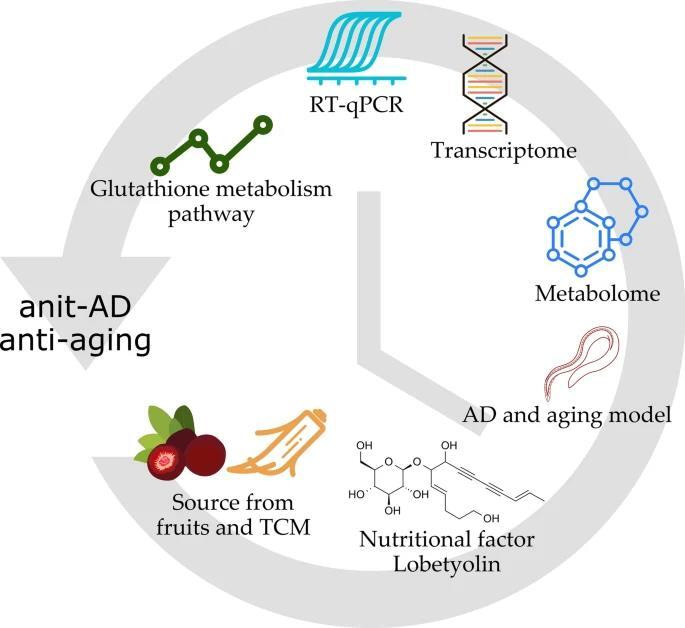
Lobetyolin, a polyacetylene glycoside derived from Codonopsis pilosula, is emerging as a promising natural candidate for Alzheimer’s disease prevention and healthy aging. In Aβ-expressing and wild-type Caenorhabditis elegans models, Lobetyolin significantly reduced β-amyloid deposition, delayed paralysis, lowered intracellular ROS levels, and extended lifespan. Integrated metabolomic and transcriptomic analyses identified glutathione-centered redox regulation as its principal mechanism, including selective modulation of GST isoforms such as gst-1 and gst-38. These redox improvements are consistent with reduced Aβ toxicity and enhanced stress resistance. Owing to its natural abundance in dietary materials like Codonopsis radix, Lobetyolin also holds potential as a food-derived neuroprotective factor. However, the lack of mammalian efficacy data and pharmacokinetic characterization currently limits translational interpretation. Future research should confirm therapeutic effects in rodent models, determine brain exposure and PK/PD profiles, and conduct comprehensive safety evaluations. Overall, this study provides mechanistic insight and a clear foundation for advancing Lobetyolin as a nutraceutical candidate for AD prevention and aging-related interventions.
Follow the Topic
-
Natural Products and Bioprospecting

This is a single blind peer-reviewed open access journal that devoted to rapidly disseminate research results in all areas of natural products.





Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in
This manuscript provides compelling evidence that Lobetyolin mitigates Aβ‑induced toxicity and oxidative stress in Caenorhabditis elegans, supported by coherent multi‑omics analyses. The identification of glutathione‑centered redox metabolism as a key intervention pathway offers a solid mechanistic basis for future mammalian investigations.