Tumor-targeted nanodrug FSGG/siGal-9 for transdermal photothermal immunotherapy of melanoma
Published in Cancer

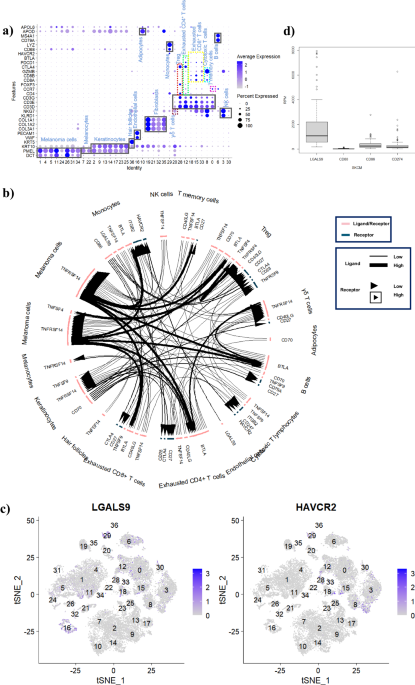
T cells in the context of cancer become exhausted and dysfunctional due to persistent immune checkpoints/co-inhibitory signals such as PD-L1/PD-1, Gal-9/TIM-3, HVEM/BTLA, and CD155/TIGIT pathways. Exhausted T cells lose robust effector functions, express IRs including PD-1, TIM-3, BTLA, CTLA-4, LAG-3, TIGIT, and decline in the secretion of functional cytokines IFN-γ, TNF-α and IL-2. It is discovered that exhausted T cells are responsive to reinvigoration of immune responses by blockade of the PD-L1/PD-1 pathway. For melanoma clinic treatment, two anti-PD-1 antibodies, nivolumab and pembrolizumab, were approved by the US FDA in 2014 for the treatment of metastatic melanoma but have been shown to produce objective response in just 30-40% of patients. In 2019, studies discovered that Gal-9/TIM-3 pathway is the key mechanism of resistance to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in lung cancer patients.
Gal-9 is highly expressed in normal tissues and associates with body immune tolerance, and was firstly evidenced with much higher expression on the primary solid tumors than CD80/86 (B7) and CD274 (PD-L1) here, which suggests that Gal-9 may be a key factor in inhibiting the anti-tumor immunity, and its receptor T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain 3 (TIM-3) was discovered on CTL with high expression as well based on the single cell analysis. The immune checkpoint communications showed that the Gal-9/TIM-3 axis played the most vital role on negatively regulating the anti-tumor immunity of CTL for melanoma.
Then, we used a novel transdermal photothermal nanosensitizer (FSGG) loading Gal-9 siRNA (FSGG/siGal-9) for knocking the tumor cells down Gal-9 to block the Gal-9/TIM-3 axis and prohibit CTL exhaustion synergizing PTT against melanoma, which evidenced good effects on inhibiting tumor growth and enhancing anti-tumor immunity, named “photothermal immunotherapy”. The nanostructure FSGG/siGal-9 possesses comparative photothermal effects with GNR, proper size about ~111.67 nm diameter, good targetability and biocompatibility, and easily eliminating from the body.
Besides exosomes derived from siGal-9-inhibiting immune checkpoint (Gal-9) tumor cells further promoted anti-tumor immunity for the photothermal immunotherapy, although heat (44 oC)-treated tumor cells are induced to release more exosomes.
This paper provides a new perspective for tumor prevention and treatment.
Abbreviations:
PD-L1: Programmed death ligand 1; PD-1: Programmed death 1; Gal-9: Galectin-9; TIM-3: T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain 3; HVEM: Herpesvirus entry mediator; BTLA: B and T lymphocyte attenuation factor; TIGIT: T cell immunoglobulin and ITIM domain protein; IRs: Inhibitory receptors; CTLA-4: Cytotoxic T lymphocyte associated antigen 4; LAG-3: Lymphocyte activation gene; IFN-γ: Interferon-γ; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; IL-2: Interleukin-2; CTL: Cytotoxic T lymphocytes; FSGG: Fe3O4@SiO2-GNR-Glu; GNR: Gold nanorod.
Follow the Topic
-
Communications Biology

An open access journal from Nature Portfolio publishing high-quality research, reviews and commentary in all areas of the biological sciences, representing significant advances and bringing new biological insight to a specialized area of research.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
From RNA Detection to Molecular Mechanisms
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: May 05, 2026
Signalling Pathways of Innate Immunity
Publishing Model: Hybrid
Deadline: May 31, 2026

Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in