Why Are Large Language Models Bad at Medical Math? The Answer May Lie in How Doctors Actually Work
Published in Computational Sciences, General & Internal Medicine, and Pharmacy & Pharmacology

The Observation: A Fundamental Problem in Medical AI
When doctors review a transplant patient or assess surgical risk, they will often use validated medical calculators rather than doing math in their heads. When we posed these types of questions to recent AI models, even advanced Al struggled with these basic calculations, getting them wrong one-third of the time. This raised an important question: Could we improve Al's performance by having it work more like doctors do?
Our Goal: We want to clarify that our focus isn't to replace a doctor's expertise, but to augment it. By combining clinical judgment with precise, rapid calculations, we think we can enhance the decision- making process without diminishing the role or value of the physician.
Building a Collaborative Team
Our team brought together diverse perspectives from Stanford Medicine and UCSF to test this hypothesis. We hypothesized that instead of just trying to make Al better at math, we should give it access to the same validated medical calculation tools clinicians use every day. But because most of these tools (that have names like MDCalc or QxMD) are made for human doctors, AI isn’t able to interact with them. To address this, we developed a set of tools that were specifically made to be used by AI, releasing it as a free web tool called OpenMedCalc.
Testing Our Hypothesis with Clinical Tools
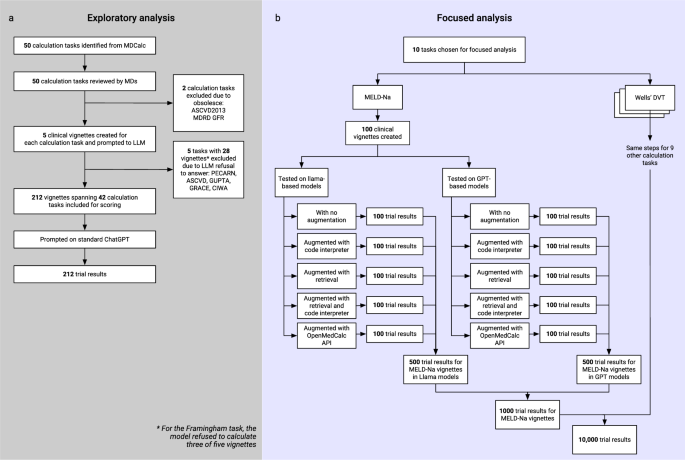
We evaluated this idea across 48 different medical calculations, from liver transplant scores to stroke risk assessments. We hypothesized that providing access to validated calculation tools would significantly improve accuracy compared to asking Al to perform calculations on its own.
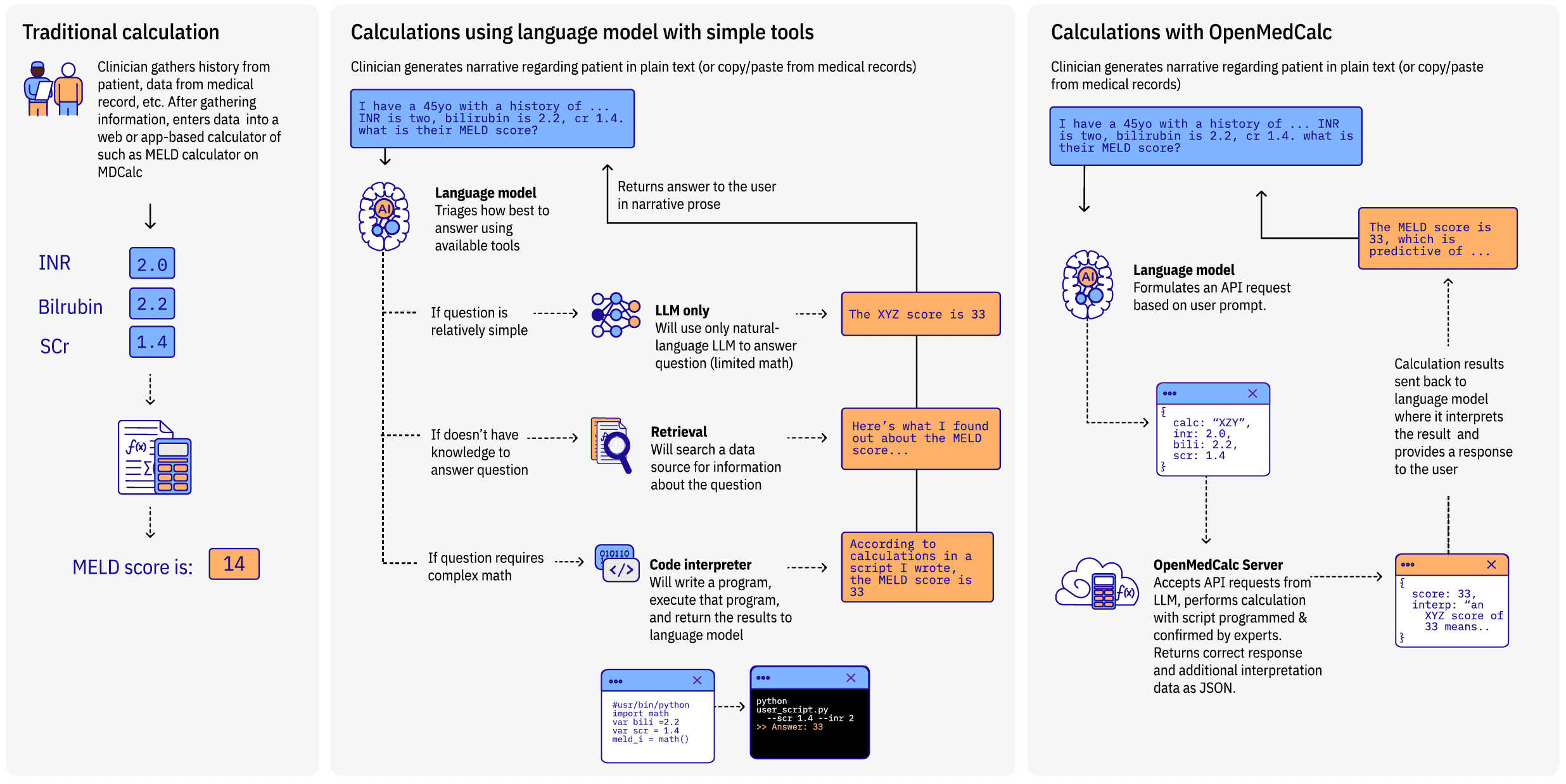
Results That Changed Our Understanding
Our approach proved transformative. When we gave Al access to these specialized medical calculators through our OpenMedCalc platform, accuracy jumped from 33% to over 95%. This leap didn't come from making Al "smarter" but from equipping it with the right resources. It underscores how supporting physicians—and now Al — with specialized tools can possibly sharpen clinical decision-making without supplanting the doctor's expertise.
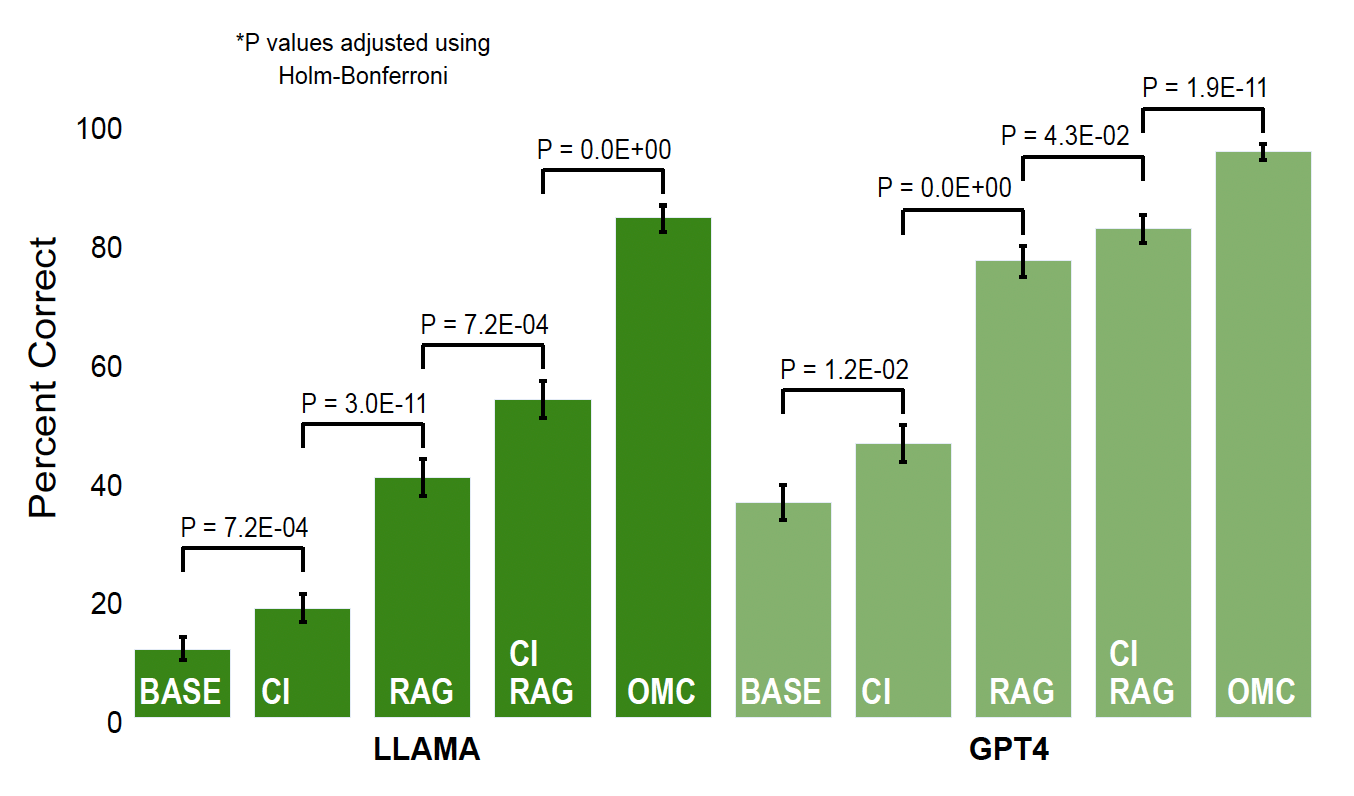
Looking Forward: Transforming Medical Calculations
While these results are exciting, we think they're just the beginning of making Al more reliable for health care. We invite you to read our complete findings in our recent Nature Digital Medicine publication, which details how this approach could help make medical Al more dependable and clinically useful.
We've made our tools freely available through OpenMedCalc because we believe in open collaboration and advancing medical Al that truly serves patients and clinicians. To learn more about this work or explore potential collaborations, please visit openmedcalc.org.
Follow the Topic
-
npj Digital Medicine

An online open-access journal dedicated to publishing research in all aspects of digital medicine, including the clinical application and implementation of digital and mobile technologies, virtual healthcare, and novel applications of artificial intelligence and informatics.
Your space to connect: The Primary immunodeficiency disorders Hub
A new Communities’ space to connect, collaborate, and explore research on Clinical Medicine, Immunology, and Diseases!
Continue reading announcementRelated Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Evaluating the Real-World Clinical Performance of AI
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Jun 03, 2026
Impact of Agentic AI on Care Delivery
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Jul 12, 2026
Latest Content
Why is Singapore Identified in Global Research as Number One? How Physical Activity and Education Excellence Created a Global Leader




Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in