A New WiMAX/Wi-Fi Interoperability Model and Its Performance Evaluation
Published in Wireless Personal Communications, 3 March 2013
Published in Computational Sciences
Like
Be the first to like this
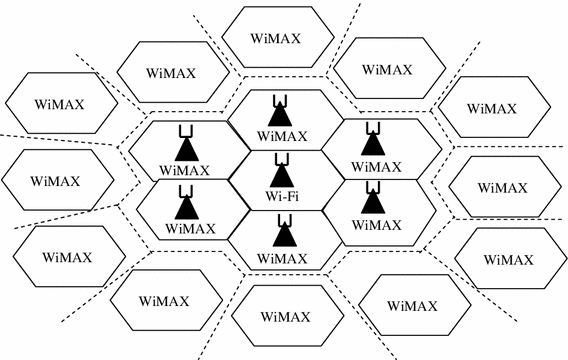
In this paper, a new interoperability model for deployment of the emerging IEEE 802.16; WiMAX (World Wide Interoperability for Microwave Access) and a Wi-Fi (Wireless Fidelity), IEEE 802.11 based on Wireless LAN technology in a complementary way as a path to migration towards the upcoming fourth generation, is presented. The model allows for the integration of the two technologies, combining the benefits of both worlds for Non line-of-sight environments. The suggested scenario is to have a hotspot Wi-Fi or urban cell surrounded by a set of WiMAX (suburban) cells where users can have continuous connectivity in different propagation environments. If the C/I (Carrier-to-Interference) of a user is higher than a given threshold (say C/I G) then the user connects to the Wi-Fi cell otherwise the user is admitted to a WiMAX cell. In both cases, the user will have the best of the available access technology with an acceptable level of grade-of-service, i.e. 2 %, on move. The suggested model includes mixed services support i.e. voice, data and video with mobility, as well as scalability based on scalable orthogonal frequency division multiplexing adaptive bandwidth allocation. The scalability is applied on data connection, where ongoing data connection is asked to modify its transmission rate for the sake of handover calls. Numerical results from the evaluation of the interoperability model are given. The curves for average data rate, utilization, blocking probability, handover blocking probability, grade of service, and throughput demonstrate the effectiveness of the new deployment model.
Follow the Topic
Computer Engineering and Networks
Mathematics and Computing > Computer Science > Computer Engineering and Networks
-
Wireless Personal Communications

An archival, peer reviewed, scientific and technical journal addressing mobile communications and computing. The Wireless Personal Communications journal investigates theoretical, engineering, and experimental aspects of radio communications, voice, data, images, and multimedia.

Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in
This is an interesting paper. Please feel free to review it and include a citation if you find it relevant.
Thank you in advance.
Aymen Zreikat