Dysfunctional Protein-Protein Interactome (dfPPI): A Platform for Systems-Level Analysis of PPI Alterations in Disease
Published in Protocols & Methods and Cell & Molecular Biology
Protein-protein interactions (PPIs) are pivotal for cellular function, governing essential processes from signal transduction to gene regulation. Their dysregulation forms the core of numerous diseases, including cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. Enter Dysfunctional Protein-Protein Interactome (dfPPI) [1], a platform designed to unravel system-level alterations in proteome functionality in disease.
Decoding dfPPI: Methodology and Insights
dfPPI employs advanced chemoproteomic techniques to map out altered PPI networks within diseased cells. By dynamically capturing the interplay between proteins under stress conditions, dfPPI leverages natural epichaperomes—aberrant protein complexes arising in disease states. Using chemical probes like PU-beads and YK5-B to capture epichaperomes and proteins, combined with mass spectrometry, dfPPI identifies and quantifies these dysregulated PPIs, offering insights into disease-specific molecular signatures.
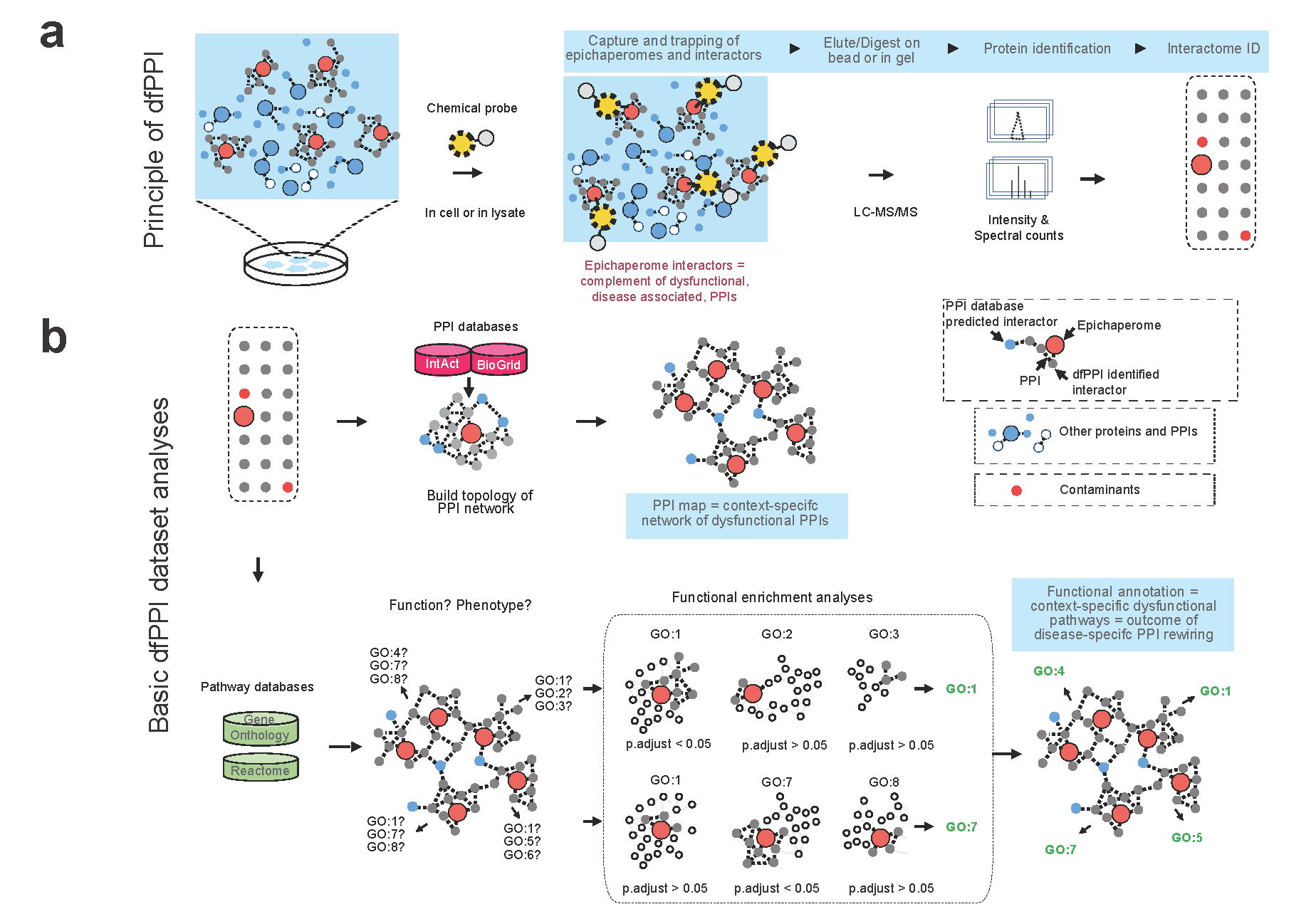
Applications in Disease Research
Cancer Insights
In oncology, dfPPI has uncovered critical dysfunctions driving tumor progression. By profiling altered PPIs, researchers have elucidated pivotal pathways essential for cancer cell survival and proliferation [2, 3]. These findings deepen our understanding of tumor biology and pinpoint potential therapeutic targets for precision medicine interventions [4].
Neurological Discoveries
In neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's, dfPPI has illuminated the molecular underpinnings of neuronal decline [5]. Through comprehensive PPI analysis, dfPPI has identified disruptions in brain function pivotal to disease progression. These insights open new avenues for therapeutic strategies aimed at preserving cognitive function and slowing disease advancement.
Conclusion
Dysfunctional Protein-Protein Interactome (dfPPI) represents a novel paradigm in disease research, providing crucial insights into the molecular complexities underlying cancer, neurodegeneration, and beyond. By unraveling altered PPI networks, dfPPI not only enhances our understanding of disease mechanisms but also catalyzes the development of targeted therapies with transformative implications for patient care.
References
1. Chakrabarty S, Wang S, Roychowdhury T, Ginsberg SD, Chiosis G. Introducing dysfunctional Protein-Protein Interactome (dfPPI) - A platform for systems-level protein-protein interaction (PPI) dysfunction investigation in disease. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2024 Jul 13;88:102886. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2024.102886. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 39003916.
2. Rodina A, Xu C, Digwal CS, Joshi S, Patel Y, Santhaseela AR, Bay S, Merugu S, Alam A, Yan P, Yang C, Roychowdhury T, Panchal P, Shrestha L, Kang Y, Sharma S, Almodovar J, Corben A, Alpaugh ML, Modi S, Guzman ML, Fei T, Taldone T, Ginsberg SD, Erdjument-Bromage H, Neubert TA, Manova-Todorova K, Tsou MB, Young JC, Wang T, Chiosis G. Systems-level analyses of protein-protein interaction network dysfunctions via epichaperomics identify cancer-specific mechanisms of stress adaptation. Nat Commun. 2023 Jun 23;14(1):3742. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39241-7. PMID: 37353488; PMCID: PMC10290137.
3. Rodina A, Wang T, Yan P, Gomes ED, Dunphy MP, Pillarsetty N, Koren J, Gerecitano JF, Taldone T, Zong H, Caldas-Lopes E, Alpaugh M, Corben A, Riolo M, Beattie B, Pressl C, Peter RI, Xu C, Trondl R, Patel HJ, Shimizu F, Bolaender A, Yang C, Panchal P, Farooq MF, Kishinevsky S, Modi S, Lin O, Chu F, Patil S, Erdjument-Bromage H, Zanzonico P, Hudis C, Studer L, Roboz GJ, Cesarman E, Cerchietti L, Levine R, Melnick A, Larson SM, Lewis JS, Guzman ML, Chiosis G. The epichaperome is an integrated chaperome network that facilitates tumour survival. Nature. 2016 Oct 20;538(7625):397-401. doi: 10.1038/nature19807. Epub 2016 Oct 5. PMID: 27706135; PMCID: PMC5283383.
4. Joshi S, Gomes ED, Wang T, Corben A, Taldone T, Gandu S, Xu C, Sharma S, Buddaseth S, Yan P, Chan LYL, Gokce A, Rajasekhar VK, Shrestha L, Panchal P, Almodovar J, Digwal CS, Rodina A, Merugu S, Pillarsetty N, Miclea V, Peter RI, Wang W, Ginsberg SD, Tang L, Mattar M, de Stanchina E, Yu KH, Lowery M, Grbovic-Huezo O, O'Reilly EM, Janjigian Y, Healey JH, Jarnagin WR, Allen PJ, Sander C, Erdjument-Bromage H, Neubert TA, Leach SD, Chiosis G. Pharmacologically controlling protein-protein interactions through epichaperomes for therapeutic vulnerability in cancer. Commun Biol. 2021 Nov 25;4(1):1333. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02842-3. PMID: 34824367; PMCID: PMC8617294.
5. Inda MC, Joshi S, Wang T, Bolaender A, Gandu S, Koren Iii J, Che AY, Taldone T, Yan P, Sun W, Uddin M, Panchal P, Riolo M, Shah S, Barlas A, Xu K, Chan LYL, Gruzinova A, Kishinevsky S, Studer L, Fossati V, Noggle SA, White JR, de Stanchina E, Sequeira S, Anthoney KH, Steele JW, Manova-Todorova K, Patil S, Dunphy MP, Pillarsetty N, Pereira AC, Erdjument-Bromage H, Neubert TA, Rodina A, Ginsberg SD, De Marco Garcia N, Luo W, Chiosis G. The epichaperome is a mediator of toxic hippocampal stress and leads to protein connectivity-based dysfunction. Nat Commun. 2020 Jan 16;11(1):319. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-14082-5. PMID: 31949159; PMCID: PMC6965647.



Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in