Room-temperature waveguide integrated quantum register in a semiconductor photonic platform

Our recent research, as published in Nature Communications, details the successful integration of entangled quantum registers into silicon-carbide-on-insulator (SiCOI) waveguides. This milestone is a significant stride towards realizing scalable quantum photonic applications.
We have demonstrated the generation of single divacancy electron spins and the initialization of single 13C nuclear spins with high precision. The ability to coherently control electron and nuclear spins is a fundamental aspect of quantum entanglement, vital for quantum computing and communication. Under ambient conditions, we managed to prepare a maximally entangled state with a remarkable fidelity of 0.89, showcasing the stability of our quantum register.
Integrating these entangled quantum registers into SiC photonic waveguides is a complex challenge. By utilizing nanoscale positioning techniques, we preserved the intrinsic optical and spin characteristics of the register, ensuring that the fidelity of the entangled state remains high at 0.88 even after integration.
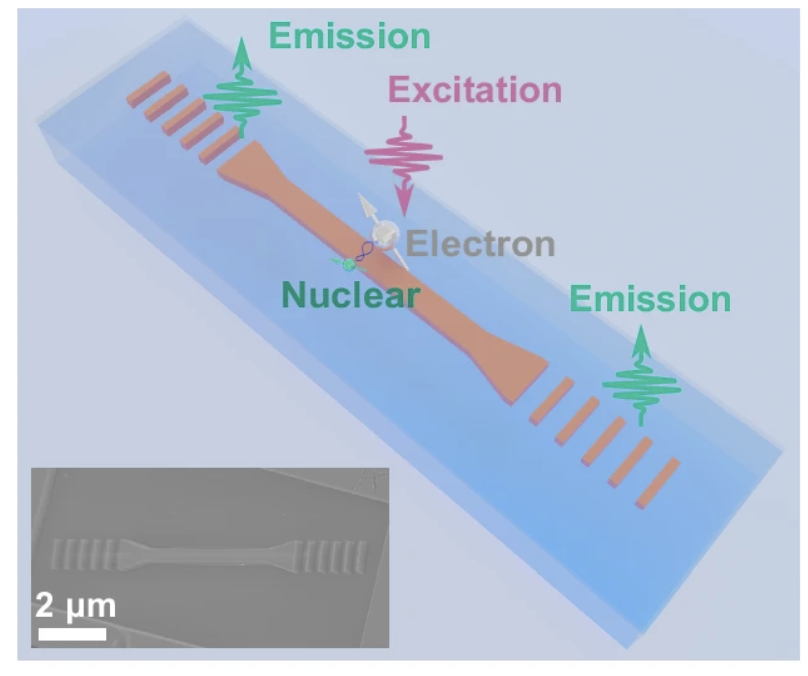
This achievement highlights the potential of the SiCOI platform for future quantum photonic applications. While challenges remain in fully integrating entangled registers into photonic devices on a CMOS-compatible platform, our findings offer a promising approach. We are excited about the prospects of enhancing coherence times and exploring the implications for quantum sensing and networking.
Additionally, I would like to share that we have successfully captured the register's emission using our custom-built CCD system. As the video below demonstrates, you can observe a tiny emitter beside cross markers. The spot marks the emission from an entangled photon originating from a SiC quantum register.
.gif)
Article Information
Hu, H., Zhou, Y., Yi, A. et al. Room-temperature waveguide integrated quantum register in a semiconductor photonic platform. Nat Commun 15, 10256 (2024)
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-54606-2
Article link: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-54606-2
Follow the Topic
-
Nature Communications

An open access, multidisciplinary journal dedicated to publishing high-quality research in all areas of the biological, health, physical, chemical and Earth sciences.
Ask the Editor – Space Physics, Quantum Physics, Atomic, Molecular and Chemical Physics
Got a question for the editor about Space Physics, Quantum Physics, Atomic, Molecular and Chemical Physics? Ask it here!
Continue reading announcementRelated Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Women's Health
Publishing Model: Hybrid
Deadline: Ongoing
Advances in neurodegenerative diseases
Publishing Model: Hybrid
Deadline: Mar 24, 2026


Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in