Sleeping beasts
Published in Astronomy
Many neutron stars are known to have magnetic fields, but magnetars have the strongest fields reaching values of 1015 G. In our research we study the structure of their magnetic field and how it forms the surface temperature patterns of these weird stars.
Magnetars are usually known for their transient behaviour, such as bursts and flares. Some of these objects can briefly outshine the whole Galaxy during a giant flare. In their normal, so-called ‘quiescent’ state, magnetars emit thermal X-ray emission. This emission modulates strongly with amplitudes of 16-53%. What could cause these periodic fluctuations?
In earlier research it was suggested that the surface of magnetars is covered with a few hot spots. These hot spots might have different sizes and different temperatures and they are not located at opposite poles. It was suggested that hot spots could appear due to a specific magnetic field configuration or heating by currents floating in the magnetosphere of the neutron star.
The magnetic fields heat the crust though its Ohmic decay and also govern how this heat flows throughout the crust, by inhibiting diffusion perpendicular to magnetic field lines. Crustal regions with radial field lines cool rapidly, whereas heat remains trapped in regions of tangential field lines. Therefore, the magnetic fields are crucial in formation of the surface thermal patterns.

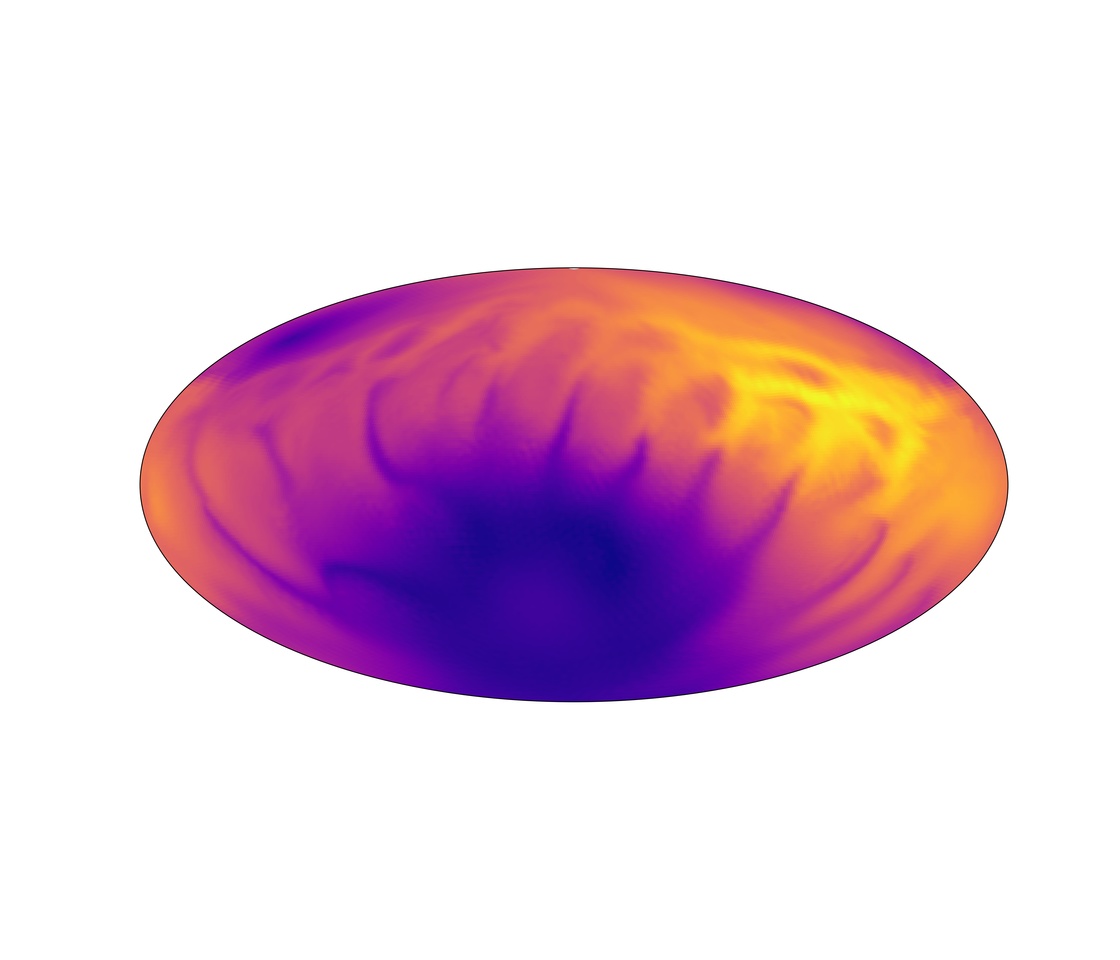
Temperatures at surface of neutron star with pure poloidal magnetic field at age 10 thousand years.
For the first time we model the magneto-thermal evolution of neutron stars in three dimensions. We vary the configuration of the crust confined magnetic field using the pure poloidal configuration, and configurations with more significant contribution of the toroidal magnetic field. In the case of pure poloidal magnetic field configuration, we noticed that the surface thermal distribution is mostly symmetric. The equatorial region is hot. We calculated that this configuration can produce maximum pulsed fraction less than 20% which is not enough to explain the fluctuation of the magnetar quiescent emission.
We also model configurations where the crust confined toroidal magnetic field contains 90% of total magnetic energy. In this case the hot region is either shifted toward one hemisphere as it is seen in one of our simulation or a single hot spot is formed. The single hot spot is formed when the axis of the large-scale toroidal magnetic field is misaligned with axis of the poloidal dipolar magnetic field. This configuration could produce pulsed fraction up to 53% which explains most emission pattern. Therefore, even without magnetospheric heating, the crust confined magnetic field evolution can explain properties of quiescent emission from magnetars.
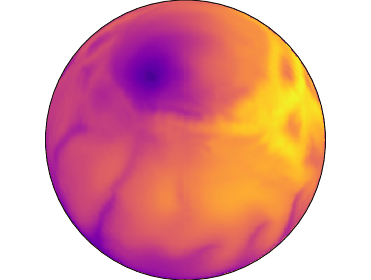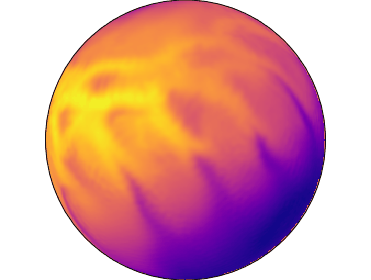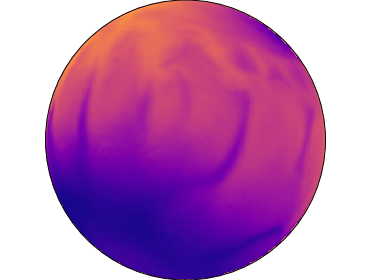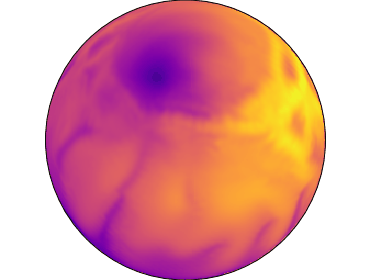
Temperatures at surface of neutron star with 90% of energy stored in toroidal magnetic field at age 24 thousand years. The poloidal magnetic field is inclined by 45 degrees in respect to the toroidal magnetic field.
Follow the Topic
-
Nature Astronomy

This journal welcomes research across astronomy, astrophysics and planetary science, with the aim of fostering closer interaction between the researchers in each of these areas.
Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in