Entrepreneurs’ Competency, Marketing Innovation, and Enterprise Growth
Published in Business & Management
A recent study, "Entrepreneurs' Competency, Marketing Innovation, and Enterprise Growth: Uncovering the Mediating Role of Marketing Innovation," delves into the intricate relationship between entrepreneurial competency, innovation, and MSMEs growth.
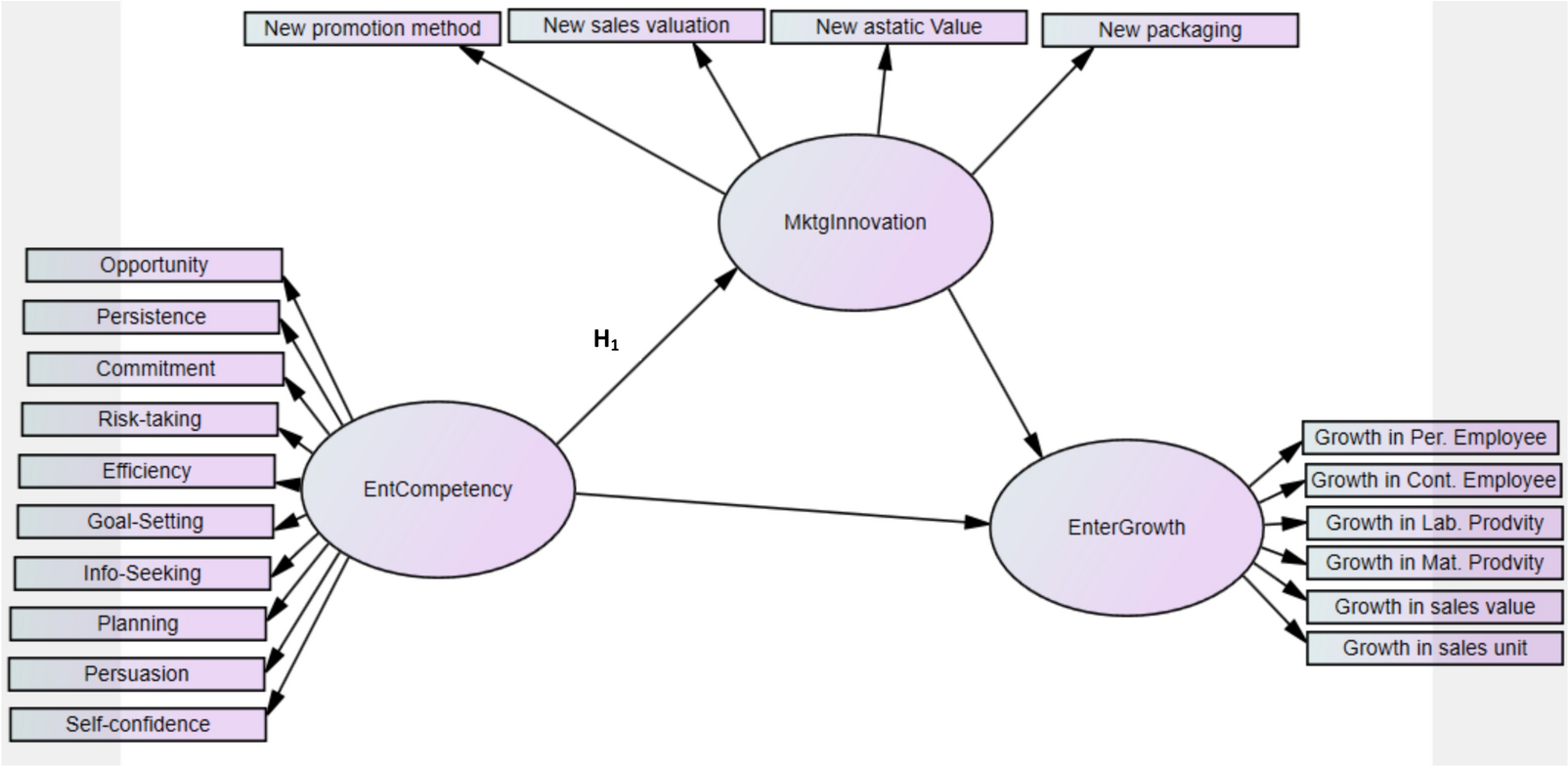
Using data from MSMEs managers in Ethiopia, the study revealed that an entrepreneur's competencies directly influence their enterprise's growth trajectory. Furthermore, the study examined the mediating role of marketing innovation in this process. While researchers hypothesized that competency would influence innovative activities, the study found that entrepreneurs were not giving sufficient attention to marketing innovation as a key factor in enhancing their enterprise's performance.
Marketing innovation serves as a bridge between entrepreneurial capability and enterprise performance. It involves applying creative thinking to marketing processes, strategies, and practices. This can include developing new marketing methods or significantly improving existing ones.
The study hypothesized that when entrepreneurs apply their competencies to innovate in marketing, they can unlock new levels of growth for their enterprises. This is because marketing innovation was assumed to lead to better market penetration, higher customer satisfaction, and increased sales and profits.
The study's findings indicate that an entrepreneur's competency significantly contributes to business growth. However, the research also highlights that the influence of competency on innovation and the impact of innovation on business growth did not show significant evidence. This suggests that while competency directly drives business expansion, the role of innovation in this process is not as clear-cut. The limited influence of competency on marketing innovation and the limited impact of marketing innovation itself implies that entrepreneurs may be overlooking the integration of innovative marketing techniques, assuming their current products will continue to sell. This mindset may be myopic and could potentially expose their business to future risks. For entrepreneurs on the ground, this means focusing on honing their entrepreneurial skills is commendable and engaging in continuous innovation as their marketing strategies should not be ignored. It's about creating a culture where innovation is not an afterthought but a fundamental aspect of the marketing approach to serve the purpose of enterprises in the long run.
In conclusion, the research emphasizes the critical role of entrepreneurs' competencies in supporting enterprise growth. It also serves as a call to action for entrepreneurs to incorporate innovation into every aspect of their business operations if they aim to scale new heights in today's competitive market landscape.
Follow the Topic
-
Future Business Journal

This is an open access, peer-reviewed journal publishing theoretical and empirical research papers covering the major aspects of management, accounting, economics, management information systems and finance.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Entrepreneurial Ecosystems and Economic Development
The concept of entrepreneurial ecosystems has gained significant traction in recent years, emphasizing the interconnectedness of various actors—such as startups, investors, policy-makers, and support organizations—that collectively contribute to economic development. These ecosystems provide a framework for understanding how innovative businesses can thrive within a supportive environment, fueled by the interplay of resources, networks, and local culture. By studying these dynamic ecosystems, researchers can uncover best practices and strategies that enhance the viability of entrepreneurial ventures and regional innovation systems.
The exploration of entrepreneurial ecosystems is crucial in today's rapidly changing economic landscape. Advances in understanding these ecosystems have led to the development of more effective policies and practices that foster startup growth, promote entrepreneurial finance, and support incubators and accelerators. Additionally, researchers are uncovering the importance of inclusive growth, ensuring that underrepresented communities can benefit from economic opportunities. This body of work contributes not only to the academic discourse but also offers practical implications for policymakers seeking to stimulate sustainable economic development.
Continued research in this field holds promise for refining the frameworks that underpin entrepreneurial ecosystems, potentially leading to innovative policies that enhance regional resilience and adaptability. As researchers delve deeper into the roles of innovation clusters and policy-driven entrepreneurship, there may be new pathways for addressing economic disparities and ensuring that entrepreneurship is accessible to all segments of society.
Short list of topic of interests:
- The role of incubators and accelerators in startup success
- Impact of entrepreneurial finance on regional innovation
- Policy-driven entrepreneurship for sustainable growth
- Analysis of innovation clusters and their economic impact
This Collection supports and amplifies research related to SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth).
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Jul 08, 2026
Internationalization and Foreign Direct Divestment Flows in Central and Eastern European Economies
Globalization has created the critical concept of internalization of firms and the world has become boundaryless world. There are many studies that are carried out on the determinants of foreign direct divestment in European Countries [EC]. But there are no much studies on foreign direct divestment in the Central and Eastern European countries. Hence, it could be concluded that studies regarding internationalization of firms especially those that are responsible for owning and operating units in foreign locations are the need of the day. The multinational companies that own and operate units in foreign locations (CEE) countries are being considered as drivers of internationalization and globalization. These multinational companies promote interdependence between Central and Eastern European countries and internationalization. They are therefore regarded as key actors in the globalization process of Central and Eastern European economies.
Despite the fact that there are many qualitative studies [non-empirical] on the determinants of foreign direct divestment, empirical [quantitative] studies on the drivers of foreign direct divestment (or foreign direct divestment inflows) are negligible in case Central and Eastern European countries. There are also limited researches [qualitative] in regard to the impact of COVID-19 on the economies of Central and Eastern European Countries. Similarly, the empirical studies on the drivers of foreign direct divestment inflows in respect of Central and Eastern European countries are also nonexistent. It is therefore, imperative to examine the post COVID-19 drivers of internationalization and foreign direct divestment [inflows] in Central and Eastern European countries.
In light of the above, this thematic issue proposes to examine the determinants of foreign direct divestment [inflows]. The investigation will be conducted through a review of the theoretical and empirical literature. The papers may use empirical model to investigate the drivers of foreign direct divestment [inflows] in the Central and Eastern European economies in particular. Panel data econometric techniques may also be used by the prospective authors to estimate the empirical model. The results of this study will have policy implications for the Central and Eastern European economies in particular. The special issue will also focus on the effects of POST-COVID-19 on the FDD inflows in Central and Eastern European Countries.
Tentative Topics:
The major thrust should be on the following issues:
Internationalization of Central and Eastern European countries;
Role and contribution of internationalization in the development of Central and Eastern European countries;
FDD Flows as a means of promoting internationalization in Central and Eastern European countries;
Pre COVID-19 FDD inflows in Centra and Eastern European countries;
Post COVID-19 Growth pattern of FDD inflows in Central and Eastern European economies;
Factors governing and affecting FDI inflows in Central and Eastern European economies;
Promotion of trade and investment relations among the Central and Eastern European economies;
Availability of incentives from the host countries to foreign investors under the persisting intensified competition among Central and Eastern European countries;
Post-COVID-19 FDI Policy in Central and Eastern European countries;
Emerging issues and challenges for Central and Eastern European economies for FDI inflows post COVID-19.
Time frame for the Issue:
• Launch for the Call for Papers: 1 September 2025
• Last Date of submission of papers: 28 February 2026
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: May 31, 2026




Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in