Antimicrobial Stewardship Implementation Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Acute-care settings
Published in Sustainability

I am Rasha Abdelsalam Elshenawy, I am a Clinical Pharmacist by background doing my PhD at the University of Hertfordshire in the UK. I am an Antimicrobial Stewardship (AMS) Global Lead. I have an American Board of Pharmacy with 20 years of experience, and I am certified in Antimicrobial Stewardship. I have special interests in antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and antimicrobial stewardship (AMS). I led AMS and put measures against antibiotic-resistant bacteria and 5-years AMS strategic plan. I am a director of FADIC Antimicrobial Stewardship School, which was shortlisted for the Antibiotic Guardian award (2020). This school was shared in the Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) AMR challenge in 2018. Realising the global burden of AMR has fulfilled my passion for finding possible solutions to AMR through effective implementation of AMS and improving antibiotic prescribing and education. I presented this research project at the University of Hertfordshire, School of Life and Medical Science (LMS) annual meeting in 2022 (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Poster presentation at the University of Hertfordshire School of Life and Medical Sciences (LMS) annual meeting in 2022
.png)
What SDG3 target(s) in my work and the work of the organization most closely aligned with?
Antibiotics are widely administered for various indications, leading to increased antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in acute care hospitals. Since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, Antimicrobial Stewardship (AMS) effective strategies should be used to maintain the rational use of antibiotics and decrease the threat of Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR).
Hence, The United Nations has set target goals in this area in 2015: Goal 3 (SDG 3 is focused on "Good Health and Well-being". It aims to ensure healthy lives and promote well-being, especially in the third goal of ‘Infectious Diseases, which was a driving motivation for implementing this Project.
I am happy to share my research in Springer Nature, which is committed to supporting the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), to opening research and sharing it widely so that it reaches the audiences that need it to address grand global challenges. It highlights the work being done to tackle some of the world's greatest health challenges.
Here is a short description of my work and how it is contributed to the Sustainable Development Goals, specifically about health emergency preparedness and how it will make a difference.
In a world where medicine has advanced drastically, antimicrobial resistance has become one of the biggest threats to public health. With the emergence of multi-resistant organisms, we need to be more vigilant than ever.
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a global crisis that is likely to continue for the foreseeable future. In 2019, The Lancet reported the estimated global deaths from AMR to be 1.2 million. People are dying from common and previously treatable infections due to bacteria developing resistance to the common antibiotics used in their treatment. If the antibiotic is prescribed inappropriately, not only does it not benefit the patient, but it could also cause side effects for them, such as allergic reactions and toxicity that affects their organs. In recent years, excessive and inappropriate use of antibiotics means they are becoming less effective against serious infections.
This is where antimicrobial stewardship comes in. It is a concept that aims to promote the responsible and appropriate use of antimicrobials by healthcare professionals. The idea is that by using antibiotics judiciously, we can prevent the development of antimicrobial resistance.
Antimicrobial stewardship promotes the responsible use of antibiotics to prevent antimicrobial resistance (AMR). By optimizing antibiotic use, healthcare professionals can mitigate the development of AMR. This could be achieved by implementing antimicrobial stewardship strategies.
The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the importance of stewardship in preventing a looming AMR crisis. Empirical data is crucial to understand and enhance antimicrobial stewardship's impact during health emergencies.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, many bacterial infections went potentially undiagnosed and untreated. The COVID-19 pandemic has taught us hard lessons and reminded us that AMS is the best way to prevent a looming AMR silent pandemic. Although, evidence is scarce on its actual effects. It is paramount to obtain empirical data to evaluate the effect of the pandemic/crisis on AMS. This will help to draw a plan to prevent and mitigate the effect of a crisis/pandemic on AMS and its impact on AMR.
Why are these goals significant to me, my organisation and their mission?
It all started with my passion for Antimicrobial Stewardship and feeling responsible towards the inappropriate use of antibiotics. I was frustrated by the rampant misuse of antibiotics and decided to take matters into his own hands. I advocated antimicrobial stewardship and worked tirelessly to promote this concept. I educated healthcare professionals and encouraged them to adopt a more judicious approach towards antimicrobial use.
I want to contribute significantly to providing a better understanding of Antimicrobial Stewardship and finding a possible solution for Antimicrobial Resistance to save patient lives. This research project will measure the AMS implementation before and during the COVID-19 pandemic, which will help to draw a plan to prevent and mitigate the effect of a crisis/pandemic on AMS and its impact on AMR.
This research project is sponsored by the University of Hertfordshire (UH), School of Life and Medical Sciences (LMS), United Kingdom, Department of Pharmaceutical Science, with the mission of firmly believing that promoting gender equality and establishing a fair and inclusive environment for staff and students ultimately results in improving the work and study environment for everyone, both men and women. LMS is dedicated to training new scientists, practitioners, and professionals ready to tackle many of today's challenges.
Where is the project(s) based, and what groups are involved?
The Health Research Authority, under reference 314805, has granted ethics approval for this research project. It is conducted at Bedfordshire Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust.
Figure 2 shows the research group, which consists of Rasha Abdelsalam Elshenawy (in the middle), the Principal Investigator and doctorate researcher. Dr Nikkie Umaru (on the left), the academic supervisor and Dr Zoe Aslanpour discuss the Chief Investigator and the principal supervisor (on the right). This research project has been registered with the ISRCTN registry, investigating the factors affecting the Antimicrobial Stewardship (AMS) implementation in acute care settings before and during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Figure 2. Photo for the research group
%20red.png)
What are the goal and objectives of the project(s)?
The goal of this research project
The project's overarching goal is to add to the body of knowledge in AMS implementation and offers practical ways to apply AMS, especially during a crisis.
Objectives
- To investigate AMS implementation in acute-care settings for adult patients' BP and DP.
- To Identify effective AMS implementation strategies BP and DP.
- To Explore HCPs’ knowledge, perception and views towards antibiotic prescribing BP and DP.
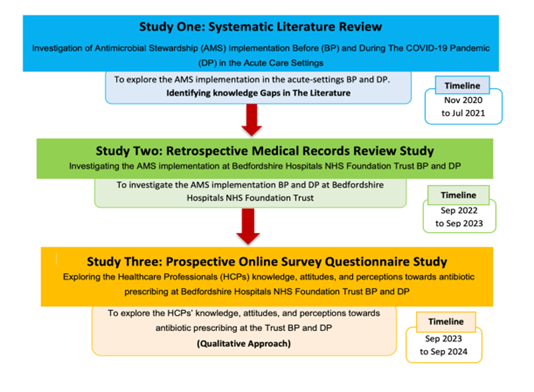
Three sequential studies will be undertaken to address the research objectives, which are illustrated in the following flow diagram (Figure 3).
- The first study aims to explore AMS interventions before and after the COVID-19 pandemic in acute care settings.
- The second study aims to investigate the practice of AMS implementation before and during the COVID-19 pandemic at Bedfordshire Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust.
- The third study will explore healthcare professionals (doctors, pharmacists, and nurses) knowledge, attitudes, and perceptions toward antibiotic prescribing and AMS implementation before and during the COVID-19 pandemic at Bedfordshire Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust.
Figure 3. Description of the research project three studies
What are the relevant measures of success I am using to determine if the goals of my project are achieved?
- Understand the AMS implementation before and during the COVID-19 pandemic at Bedfordshire Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust.
- Measure the AMS implementation before and during the COVID-19 pandemic by identifying the AMS intervention strategies that could be used in the future to achieve better preparedness for emergencies/crises.
- Offer a practical way to apply AMS, especially during an emergency or crisis, and identifies the perceived impact of interventions used in implementing AMS to decrease the AMR threat and save patient lives.
- Add to the body of knowledge in AMS implementation as well as inform policy.
- Draw a plan to prevent and mitigate the effect of any crisis/pandemic on AMS and its impact on AMR.
- Identify antibiotic prescribing trends during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Follow the Topic
-
ISRCTN: The UK’s Clinical Study Registry

A primary clinical trial registry recognised by WHO and ICMJE that accepts studies involving human subjects or populations with outcome measures assessing effects on human health and well-being, including studies in healthcare, social care, education, workplace safety and economic development.
What are SDG Topics?
An introduction to Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Topics and their role in highlighting sustainable development research.
Continue reading announcement





Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in