Mevalonate pathway inhibition reduces bladder cancer metastasis by modulating RhoB protein stability and integrin β1 localization
Published in Cancer
This study investigates how cholesterol production, specifically through the mevalonate (MVA) pathway, affects the spread and severity of bladder cancer (BLCA). Cholesterol is crucial for maintaining cell membrane integrity [1] and is synthesized via the MVA pathway, which has been linked to cancer metastasis [2,3]. Our previous research showed that simvastatin, a drug that blocks a key enzyme in the MVA pathway, can reduce the risk and slow the spread of BLCA [4,5].
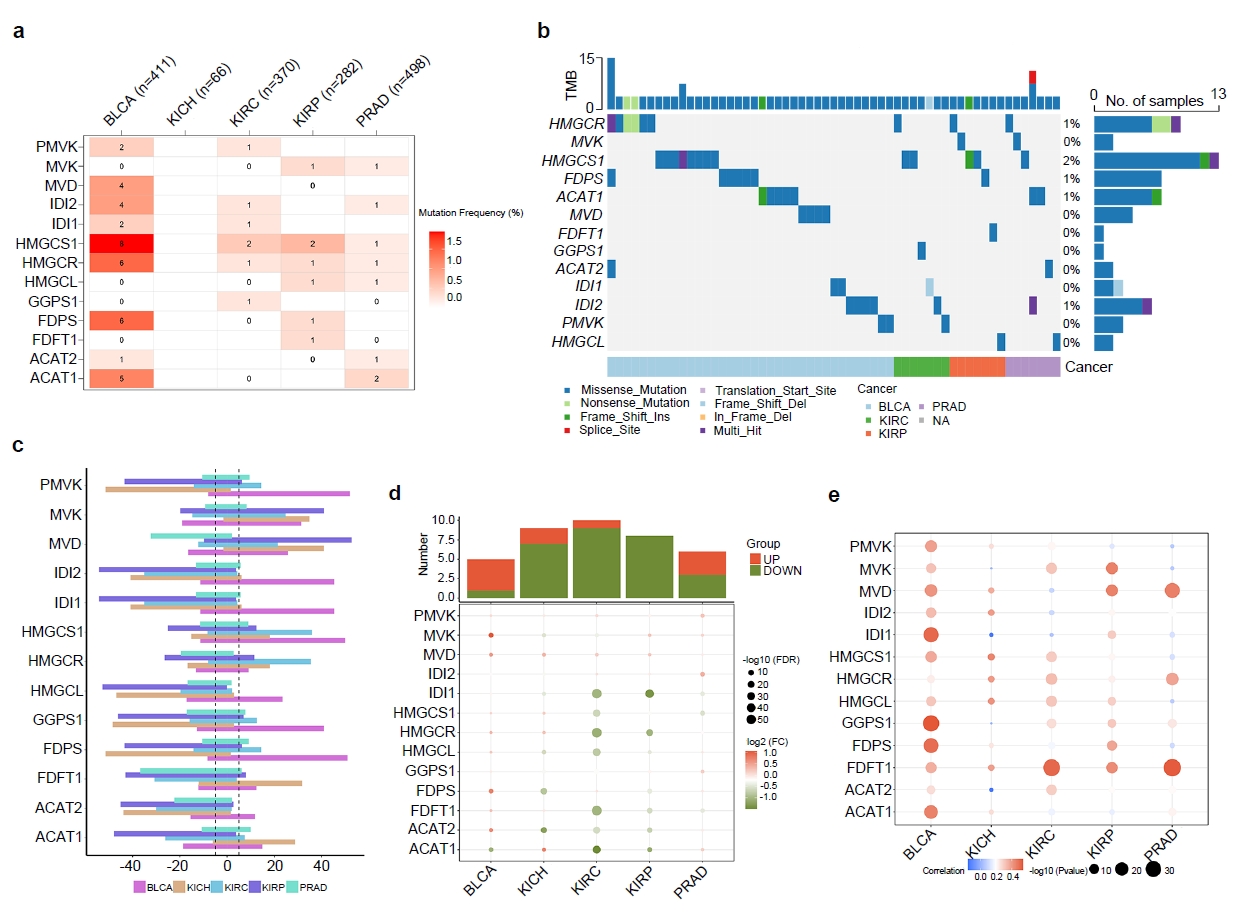
We analyzed genetic data from various urologic cancers and found that the enzymes involved in the MVA pathway are more active in BLCA than in other types. Our findings suggest that high activity of this pathway in BLCA correlates with worse patient outcomes.
We focused on farnesyl diphosphate synthase (FDPS), an important enzyme in this pathway, examining its levels in BLCA tissues and its impact on patient survival. Elevated FDPS levels were linked to poorer survival. We discovered that FDPS stability in BLCA cells is controlled by a specific protein degradation system.
By reducing the activity of the MVA pathway or using drugs like simvastatin, we could decrease the migration of BLCA cells. This effect was connected to changes in RhoB protein levels, which play a crucial role in controlling cancer cell movement and spread.

Our results highlight that targeting the MVA pathway could be a promising approach to prevent or treat the spread of BLCA. This pathway's influence on RhoB proteins and their interaction with cell membrane components like integrin β1 might be key mechanisms through which BLCA spreads and worsens.
This study was conducted by Drs. Yu Xiao and Xinghuan Wang, with contributions from Drs. Gang Wang, Tianchen Peng, and Liang Chen.
References
[3] Guerra B, et al. The Mevalonate Pathway, a Metabolic Target in Cancer Therapy. Front Oncol 11, 626971 (2021).
[4] Wang G, et al. Simvastatin induces cell cycle arrest and inhibits proliferation of bladder cancer cells via PPARgamma signalling pathway. Sci Rep 6, 35783 (2016).
[5] Wei H, et al. Unveiling the association between HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and bladder cancer: a comprehensive analysis using Mendelian randomization, animal models, and transcriptomics. Pharmacogenomics J 24, 24 (2024).
Follow the Topic
-
Communications Biology

An open access journal from Nature Portfolio publishing high-quality research, reviews and commentary in all areas of the biological sciences, representing significant advances and bringing new biological insight to a specialized area of research.
Related Collections
With Collections, you can get published faster and increase your visibility.
Signalling Pathways of Innate Immunity
Publishing Model: Hybrid
Deadline: Feb 28, 2026
Forces in Cell Biology
Publishing Model: Open Access
Deadline: Apr 30, 2026


Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in